A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 36857834
- PMCID: PMC9942450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2023.02.021
A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
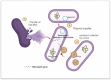
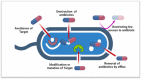
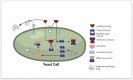
World is in the middle of the pandemic (COVID-19), caused by SARS-COV-2 virus, which is a significant global health crisis after Spanish influenza in the beginning of 20th century. Progressive drastic steps have been enforced to minimize the transmission of the disease. Likewise, in the current years, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been referred as one of the potential perils to the global economy and health; however, it is now veiled under the present pandemic. During the current pandemic, AMR to available frontline antibiotics may prove fatal and life threatening to bacterial and fungal infections during routine procedures like elective surgery, C-sections, etc. Currently, a swift elevation in multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), like carbapenem-resistant New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM)-producing Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacterales, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), multi-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and pan-echinocandin-resistant Candida glabrata has been seen. Thereupon, the global outbreak of COVID-19 also offers some important ramification for developing antimicrobial drug resistance. This article aims to highlights episodes and aspects of AMR prevalence, impact of management and mismanagement of COVID-19 crisis, hospital settings, community, environment, and travel on the AMR during the current pandemic.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR); Bacteria; Covid-19; Disinfectants; Fungi; Travel.
Copyright © 2023 The Author. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Rossen J.W.A., Tedim A.P., Murray A.K. The novel coronavirus COVID-19 outbreak: global implications for antimicrobial resistance. Front Microbiol. 2020;1:1020. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01020. 〈www.frontiersin.org〉 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

