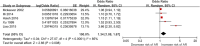Early exposure to infections increases the risk of allergic rhinitis-a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36859178
- PMCID: PMC9976500
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-023-03870-0
Early exposure to infections increases the risk of allergic rhinitis-a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to provide evidence for early life care by meta-analyzing the relationship between infection during pregnancy and up to 2 years of age and the risk of subsequent allergic rhinitis (AR).
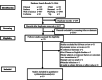
Methods: Published studies up to April 2022 were systematically searched in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, SinoMed, CNKI, Wanfang Database, and VIP. Literature screening, including quality assessment, was performed, and the effect values (OR, HR, RR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of infection during pregnancy and up to 2 years of age and allergic rhinitis were extracted from each qualified study.
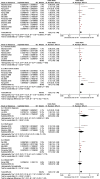
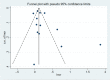
Results: In total, 5 studies with a sample size of 82,256 reported the relationship between infection during pregnancy and offspring AR. Meta-analysis showed that maternal infection during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk of childhood AR in offspring (OR = 1.34, 95% CI: 1.08-1.67). Altogether, 13 studies with a sample size of 78,426 reported evidence of an association between infection within 2 years of age and subsequent AR in children. A pooled meta-analysis of all studies showed that early infection within 2 years of age was closely associated with childhood AR (OR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.12-1.40), especially upper respiratory tract infection (OR = 1.32, 95% CI: 1.06-1.65) and gastrointestinal infections (OR = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.01-1.86), but ear infection showed similar results in the cohort study (OR = 1.13, 95% CI: 1.04-1.22).
Conclusion: Current evidence suggests that infection during pregnancy, early upper respiratory infection, gastrointestinal infections and ear infection within 2 years of age would increase the risk of AR in children. Therefore, the prevention of infection during pregnancy and in infancy and young children needs to be emphasized.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Children; Infections; Meta-analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Clinical Practice Guideline Diagnosis and treatment in children with allergic rhinitis. Chin J Pract Pediatr. 2019;34(03):169–175.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous