Study on the thermal stability of nab-paclitaxel during hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
- PMID: 36859304
- PMCID: PMC9979565
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-023-00653-2
Study on the thermal stability of nab-paclitaxel during hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel), as a special targeted preparation of paclitaxel, has the advantages of good curative effect and less side effects in anti-tumor therapy. The existence of the plasma-peritoneal barrier and insufficient blood supply make intravenous drugs hard to reach the peritoneum, while hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy can solve the difficulty. And compared with systemic medications, HIPEC can also give higher concentrations of chemotherapy drugs in the abdominal cavity, while ensuring lower systemic toxicity. However, at present, there is no relevant report on the clinical study of nab-paclitaxel during intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy, and its stability under special temperature conditions has not been reported either.
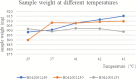
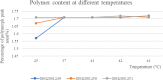
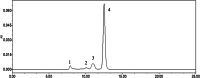
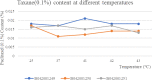
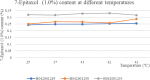
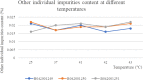
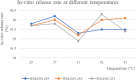
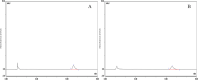
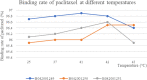
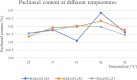
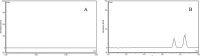
Methods: In this study, We examined three batches of albumin-bound paclitaxel dissolved in saline at different temperatures (25 °C, 37 °C, 41 °C, 42 °C and 43 °C) for the changes of human serum albumin content, human serum albumin polymer content, related substance content, in-vitro release rate, paclitaxel binding rate and paclitaxel content at different temperatures.
Results: Our results demonstrated that the indicators including human serum albumin content, human serum albumin polymer content, in-vitro release rate, paclitaxel binding rate and paclitaxel content were stable to the several temperatures, except that Taxane (0.1%) and other individual impurities in the determination of related substance content fluctuated comparatively widely with the change of temperature. In addition, only Taxane (0.1%) and 7-Epitaxol (1%) were detected.
Conclusions: Overall, albumin-bound paclitaxel is relatively stable to different temperatures (25 °C, 37 °C, 41 °C, 42 °C and 43 °C). This study will lay a foundation for further studies on the albumin-bound paclitaxel during hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.
Keywords: Albumin-bound paclitaxel; Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy; Temperature; Thermal stability.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Short-Term Safety Evaluation of Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel in Intraoperative and Postoperative Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Gastric Cancer.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024 Jun;55(2):877-887. doi: 10.1007/s12029-024-01031-9. Epub 2024 Feb 17. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38367177
-
High Penetration of Paclitaxel in Abdominal Wall of Rabbits after Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Administration of Nab-Paclitaxel Compared to Standard Paclitaxel Formulation.Pharm Res. 2017 Jun;34(6):1180-1186. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2132-4. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28247168
-
Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): An Overview of the Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Actions and Effects on Epithelial Ovarian Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 3;23(17):10078. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710078. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demonstration of treatment planning software for hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in a rat model.Int J Hyperthermia. 2021;38(1):38-54. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1852324. Int J Hyperthermia. 2021. PMID: 33487083
-
A guide to establishing a hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy program in gynecologic oncology.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Sep;158(3):794-802. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.06.487. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32624234 Review.
Cited by
-
Zwitterionic nanoparticles for thermally activated drug delivery in hyperthermia cancer treatment.Nanoscale. 2024 Jul 4;16(26):12635-12649. doi: 10.1039/d4nr00723a. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38884523 Free PMC article.
-
A Multifunctional Capsule-like Puncture Biopsy Robot for the Gastrointestinal System.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 May 18;16(5):589. doi: 10.3390/mi16050589. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428715 Free PMC article.
-
Amplifying Curcumin's Antitumor Potential: A Heat-Driven Approach for Colorectal Cancer Treatment.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Jan 30;17:63-78. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S448024. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38313386 Free PMC article.
-
The exploration of surgery and survival prediction in patients with peritoneal metastasis from gastric adenocarcinoma based on the SEER database.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;15(2):597-611. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-886. Epub 2024 Apr 28. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai H, Iwasa S, Boku N, Kawahira M, Yasui H, Masuishi T, Muro K, Minashi K, Hironaka S, Fukuda N, Takahari D, Nakajima TE. Fluoropyrimidine with or without platinum as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer and severe peritoneal metastasis: a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5720-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

