Integration of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Datasets: A Review of Computational Methods
- PMID: 36859475
- PMCID: PMC9982060
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2023.0009
Integration of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Datasets: A Review of Computational Methods
Abstract
With the increased number of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets in public repositories, integrative analysis of multiple scRNA-seq datasets has become commonplace. Batch effects among different datasets are inevitable because of differences in cell isolation and handling protocols, library preparation technology, and sequencing platforms. To remove these batch effects for effective integration of multiple scRNA-seq datasets, a number of methodologies have been developed based on diverse concepts and approaches. These methods have proven useful for examining whether cellular features, such as cell subpopulations and marker genes, identified from a certain dataset, are consistently present, or whether their condition-dependent variations, such as increases in cell subpopulations in particular disease-related conditions, are consistently observed in different datasets generated under similar or distinct conditions. In this review, we summarize the concepts and approaches of the integration methods and their pros and cons as has been reported in previous literature.
Keywords: batch correction; data integration; single-cell RNA-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

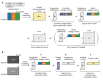
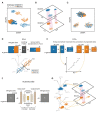
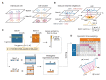


References
-
- Barrett T., Wilhite S.E., Ledoux P., Evangelista C., Kim I.F., Tomashevsky M., Marshall K.A., Phillippy K.H., Sherman P.M., Holko M., et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41((Database issue)):D991–D995. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1193. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

