Assessment of Performance, Microbial Community, Bacterial Food Quality, and Gene Expression of Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Reared under Different Density Biofloc Systems
- PMID: 36860427
- PMCID: PMC9973138
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3499061
Assessment of Performance, Microbial Community, Bacterial Food Quality, and Gene Expression of Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Reared under Different Density Biofloc Systems
Abstract
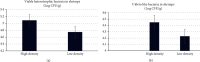
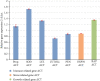
Biofloc shrimp culture, as a way of improving shrimp production, gains worldwide consideration. However, the effects of the biofloc system on shrimp culture at high densities could be a challenge. Here, this study is aimed at identifying a better stocking density of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) between two intensive biofloc systems of 100 and 300 org./m2. Achieving that was done by comparing growth performance, water quality, feed utilization, microbial loads from water and shrimps, and gene expression of growth, stress, and immune-related genes. Shrimp postlarvae with a mean weight of 35.4 ± 3.7 mg were reared in six indoor cement tanks (36 m3 total capacity each) at two stocking densities (3 replicates each) for a rearing period of 135 days. Better final weight, weight gain, average daily weight gain, specific growth rate, biomass increase percentage, and survival rate were associated with lower density (100/m2), whereas high-density showed significantly higher total biomass. Better feed utilization was found in the lower density treatment. Lower density treatment enhanced water quality parameters, including higher dissolved oxygen and lower nitrogenous wastes. Heterotrophic bacterial count in water samples was recorded as 5.28 ± 0.15 and 5.11 ± 0.28 log CFU/ml from the high- and low-density systems, respectively, with no significant difference. Beneficial bacteria such as Bacillus spp. were identified in water samples from both systems, still, the Vibrio-like count was developed in the higher density system. Regarding shrimp food bacterial quality, the total bacterial count in the shrimp was recorded as 5.09 ± 0.1 log CFU/g in the 300 org./m2 treatment compared to 4.75 ± 0.24 log CFU/g in the lower density. Escherichia coli was isolated from the shrimps in a lower density group while Aeromonas hydrophila and Citrobacter freundii were associated with shrimps from a higher density system. Immune-related genes including prophenoloxidase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and lysozyme (LYZ) expressions were all significantly higher expressed in the shrimp from the lower density treatment. Toll receptor (LvToll), penaiedin4 (PEN4), and stress-related gene (HSP 70) showed a decreased gene expression in the shrimp raised in the lower density. Significant upregulation of growth-related gene (Ras-related protein-RAP) expression was associated with the lower stocking density system. In conclusion, the current study found that applying high stocking density (300 org./m2) contributes negatively to performance, water quality, microbial community, bacterial food quality, and gene expression of immune, stress, and growth-related genes when compared with the lower stocking density system (100 org./m2) under biofloc system.
Copyright © 2022 Mohamed M. Said et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of stocking density on the growth, immune and physiological responses, and cultivation environment of white-leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in biofloc systems.Sci Rep. 2024 May 15;14(1):11147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61328-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38750082 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of stocking density of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) on immunities, antioxidant status, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in a biofloc system.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Aug;67:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.038. Epub 2017 May 15. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28522419
-
Supplementation of ex situ produced bioflocs improves immune response against AHPND in Pacific whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 May;106(9-10):3751-3764. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11966-3. Epub 2022 May 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35562491
-
A Review: Microbes and Their Effect on Growth Performance of Litopenaeus vannamei (White Leg Shrimps) during Culture in Biofloc Technology System.Microorganisms. 2024 May 17;12(5):1013. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051013. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the biofloc culture potential: Harnessing immune functions for resilience of shrimp and resistance against AHPND -causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Aug;151:109710. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109710. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38901683 Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic Sequencing Elucidated the Microbial Diversity of Rearing Water Environments for Sichuan Taimen (Hucho bleekeri).Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;15(10):1314. doi: 10.3390/genes15101314. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457438 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of stocking density on the growth, immune and physiological responses, and cultivation environment of white-leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in biofloc systems.Sci Rep. 2024 May 15;14(1):11147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61328-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38750082 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) Larvae Meal as a Carbon Source in Biofloc System for Dwarf Crayfish (Cambarellus montezumae) Culture.Aquac Nutr. 2025 Aug 6;2025:1521301. doi: 10.1155/anu/1521301. eCollection 2025. Aquac Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40809999 Free PMC article.
-
The P4' Peptide-Carrying Bacillus subtilis in Cottonseed Meal Improves the Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis Innate Immunity, Redox Defense, and Growth Performance.Aquac Nutr. 2024 Feb 12;2024:3147505. doi: 10.1155/2024/3147505. eCollection 2024. Aquac Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38374819 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics and Phytobiotics as Dietary and Water Supplements in Biofloc Aquaculture Systems.Aquac Nutr. 2024 Dec 11;2024:3089887. doi: 10.1155/anu/3089887. eCollection 2024. Aquac Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39697821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao P., Huang J., Wang X. H., et al. The application of bioflocs technology in high-intensive, zero exchange farming systems of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture . 2012;354-355:97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.03.034. - DOI
-
- Aguilera-Rivera D., Prieto-Davó A., Escalante K., Chávez C., Cuzon G., Gaxiola G. Probiotic effect of FLOC on Vibrios in the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture . 2014;424-425:215–219. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.01.008. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
