Predictive validity of the Short Functional Geriatric Evaluation for mortality, hospitalization and institutionalization in older adults: A retrospective cohort survey
- PMID: 36860714
- PMCID: PMC9969158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnss.2022.12.019
Predictive validity of the Short Functional Geriatric Evaluation for mortality, hospitalization and institutionalization in older adults: A retrospective cohort survey
Abstract
Objectives: Bio-psycho-social frailty is related to increased risk of death and utilization of health services. This paper reports the predictive validity of a 10-min multidimensional questionnaire on the risk of death, hospitalization and institutionalization.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed based on data from the "Long Live the Elderly!" program, involving 8,561 community-dwelling Italian people >75, followed for an average of 516.6 days (Median = 448, P 25-P 75: 309-692). Mortality, hospitalization, and institutionalization rates according to frailty levels assessed by the Short Functional Geriatric Evaluation (SFGE) have been calculated.
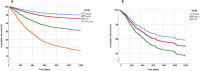
Results: Compared with the robust, the pre-frail, frail, and very frail faced a statistically significant increase in the risk of mortality (RR = 1.40, 2.78 and 5.41), hospitalization (OR = 1.31, 1.67, and 2.08) and institutionalization (OR = 3.63, 9.52, and 10.62). Similar results were obtained in the sub-sample of those with only socio-economic issues. Frailty predicted mortality with an area under the ROC curve of 0.70 (95% CI 0.68-0.72) with sensitivity and specificity of 83.2% and 40.4%. Analyses of single determinants of these negative outcomes showed a multivariable pattern of determinants for all the events.
Conclusions: The SFGE predicts death, hospitalization and institutionalization by stratifying older people according to the levels of frailty. The short administration time, the socio-economic variables and the characteristics of personnel administering the questionnaire make it suitable for being used in public health as a screening tool for a large population, to put frailty at the core of the care for community-dwelling older adults. The difficulty in capturing the complexity of the frailty is witnessed by the moderate sensitivity and specificity of the questionnaire.
Keywords: Aged; Frailty; Geriatric assessment; Italy; Surveys and questionnaires.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (Istat). Il Censimento permanente della popolazione e delle abitazioni. Prima diffusione dei dati definitivi 2018 e 2019. [Accessed 8 November 2021]. https://www.istat.it/it/files/2020/12/REPORT_CENSIPOP_2020.pdf.
-
- Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (Istat) 2019. Gli anziani e la loro domanda sociale e sanitaria anno.https://www.istat.it/it/files//2021/06/rapporto_commissione_anziani.pdf
-
- Liotta G., O'Caoimh R., Gilardi F., Proietti M.G., Rocco G., Alvaro R., et al. Assessment of frailty in community-dwelling older adults residents in the Lazio region (Italy):A model to plan regional community-based services. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017;68:1–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources