Trends in human leptospirosis in Denmark, 2012-2021
- PMID: 36860988
- PMCID: PMC9968856
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1079946
Trends in human leptospirosis in Denmark, 2012-2021
Abstract
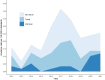
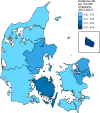
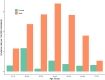
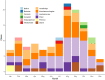
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic bacterial infection that can cause influenza-like symptoms and severe disease. In Denmark, leptospirosis is rare, non-endemic, and most commonly transferred to humans from mice and rats. Cases of human leptospirosis in Denmark are by law notifiable to Statens Serum Institut. This study aimed to describe trends in incidence of leptospirosis in Denmark from 2012 to 2021. Descriptive analyses were used to calculate the incidence, geographical distribution and possible routes of infection, as well as testing capacity and serological trends. The overall incidence rate was 0.23 per 100,000 inhabitants, with the highest annual incidence of 24 cases in 2017. Men between 40-49 years old were the demographic group most commonly diagnosed with leptospirosis. August and September were the months with highest incidence over the entire study period. The most common serovar observed was Icterohaemorrhagiae, although over a third of cases were diagnosed via polymerase chain reaction alone. The most common sources of exposure reported were travel abroad, farming, and recreational contact with fresh water, the latter being a new exposure compared to previous studies. Overall, a One Health approach would ensure better detection of outbreaks and milder disease. Additionally, preventative measures should be expanded to include recreational water sports.
Keywords: Denmark; disease surveillance; emerging disease; leptospirosis; one health (OH); zoonosis.
Copyright © 2023 Eves, Kjelsø, Benedetti, Jørgensen and Krogfelt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Danish Health Authority.(2000). Bekendtgørelse om lægers anmeldelse af smitsomme sygdomme m.v. (Copenhagen, Denmark: ).
-
- Anonymous. (2018). Annual Report on Zoonoses in Denmark 2017. (Copenhagen, Denmark: National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark; ).
-
- Eurostat. (2021). Home, GISCO, Geodata, reference data, Administrative Units / Statistical units, NUTS, 1M, EPSG: 3035 shapefile. Administrative boundaries: © EuroGeographics, © TurkStat. Source: European Commission – Eurostat/GISCO. Online. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/gisco/geodata/reference-data/administr... (accessed on: 28/12/2022). Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/gisco/geodata/reference-data/administr....
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) (2015). “Division of high-consequence pathogens and pathology (DHCPP),” in Risk of exposure. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/leptospirosis/exposure/index.html.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

