Bioengineered omental transplant site promotes pancreatic islet allografts survival in non-human primates
- PMID: 36863336
- PMCID: PMC10040375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100959
Bioengineered omental transplant site promotes pancreatic islet allografts survival in non-human primates
Abstract
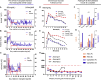
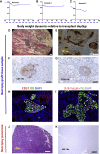
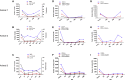
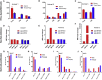
The transplanting islets to the liver approach suffers from an immediate posttransplant loss of islets of more than 50%, progressive graft dysfunction over time, and precludes recovery of grafts should there be serious complications such as the development of teratomas with grafts that are stem cell-derived islets (SC-islets). The omentum features an attractive extrahepatic alternative site for clinical islet transplantation. We explore an approach in which allogeneic islets are transplanted onto the omentum, which is bioengineered with a plasma-thrombin biodegradable matrix in three diabetic non-human primates (NHPs). Within 1 week posttransplant, each transplanted NHP achieves normoglycemia and insulin independence and remains stable until termination of the experiment. Success was achieved in each case with islets recovered from a single NHP donor. Histology demonstrates robust revascularization and reinnervation of the graft. This preclinical study can inform the development of strategies for β cell replacement including the use of SC-islets or other types of novel cells in clinical settings.
Keywords: allogeneic islet transplantation; bioengineering the omentum; euglycemia; graft survival; non-human primate; plasma-thrombin matrix; revascularization and reinnervation; single donor; stem cell-derived islets.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- CDC National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-stat...
-
- Hering B.J., Clarke W.R., Bridges N.D., Eggerman T.L., Alejandro R., Bellin M.D., Chaloner K., Czarniecki C.W., Goldstein J.S., Hunsicker L.G., et al. Phase 3 trial of transplantation of human islets in type 1 diabetes complicated by severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1230–1240. doi: 10.2337/dc15-1988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Markmann J.F., Rickels M.R., Eggerman T.L., Bridges N.D., Lafontant D.E., Qidwai J., Foster E., Clarke W.R., Kamoun M., Alejandro R., et al. Phase 3 trial of human islet-after-kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Transplant. 2021;21:1477–1492. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16174. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

