A modified ELISA assay differentiates CCL20 locked dimers from wild-type monomers
- PMID: 36863695
- PMCID: PMC10715733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2023.113453
A modified ELISA assay differentiates CCL20 locked dimers from wild-type monomers
Abstract
A novel engineered CCL20 locked dimer (CCL20LD) is nearly identical to the naturally occurring chemokine CCL20 but blocks CCR6-mediated chemotaxis and offers a new approach to treat the diseases of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Methods for quantifying CCL20LD serum levels are needed to assess pharmacokinetics parameters and evaluate drug delivery, metabolism, and toxicity. Existing ELISA kits fail to discriminate between CCL20LD and the natural chemokine, CCL20WT (the wild type monomer). Herein, we tested several available CCL20 monoclonal antibodies to be able to identify one clone that can be used both as a capture and a detection antibody (with biotin-labeling) to specifically detect CCL20LD with high specificity. After validation using recombinant proteins, the CCL20LD-selective ELISA was used to analyze blood samples from CCL20LD treated mice, demonstrating the utility of this novel assay for preclinical development of a biopharmaceutical lead compound for psoriatic disease.
Keywords: Cytokine; ELISA; Locked dimer; Psoriasis.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest STH, BFV, MBD, WFC, FCP, and CAK have financial interest in and are officers of XLock Biosciences, which produces the CCL20LD.
Figures


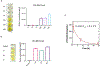
References
-
- Cochez PM, Michiels C, Hendrickx E, Dauguet N, Warnier G, Renauld JC, Dumoutier L, 2017. Ccr6 is dispensable for the development of skin lesions induced by Imiquimod despite its effect on epidermal homing of IL-22-producing cells. J Invest Dermatol 137, 1094–1103. - PubMed
-
- Ekman AK, Sigurdardottir G, Carlstrom M, Kartul N, Jenmalm MC, Enerback C, 2013. Systemically elevated Th1-, Th2- and Th17-associated chemokines in psoriasis vulgaris before and after ultraviolet B treatment. Acta Derm. Venereol 93, 527–531. - PubMed
-
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, Nakahara T, Furue M, 2020. The CCL20 and CCR6 axis in psoriasis. Scand. J. Immunol 91, e12846. - PubMed

