Expectation violations enhance neuronal encoding of sensory information in mouse primary visual cortex
- PMID: 36864037
- PMCID: PMC9981605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36608-8
Expectation violations enhance neuronal encoding of sensory information in mouse primary visual cortex
Abstract
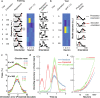
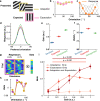
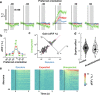
The response of cortical neurons to sensory stimuli is shaped both by past events (adaptation) and the expectation of future events (prediction). Here we employed a visual stimulus paradigm with different levels of predictability to characterise how expectation influences orientation selectivity in the primary visual cortex (V1) of male mice. We recorded neuronal activity using two-photon calcium imaging (GCaMP6f) while animals viewed sequences of grating stimuli which either varied randomly in their orientations or rotated predictably with occasional transitions to an unexpected orientation. For single neurons and the population, there was significant enhancement in the gain of orientation-selective responses to unexpected gratings. This gain-enhancement for unexpected stimuli was prominent in both awake and anaesthetised mice. We implemented a computational model to demonstrate how trial-to-trial variability in neuronal responses were best characterised when adaptation and expectation effects were combined.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

