Analysis of contact pressure in a 3D model of dual-mobility hip joint prosthesis under a gait cycle
- PMID: 36864170
- PMCID: PMC9981612
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-30725-6
Analysis of contact pressure in a 3D model of dual-mobility hip joint prosthesis under a gait cycle
Abstract
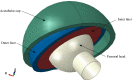
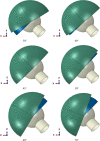
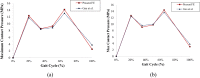
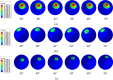
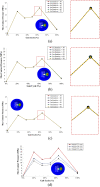
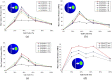
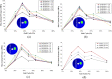
Hip joint prostheses are used to replace hip joint function in the human body. The latest dual-mobility hip joint prosthesis has an additional component of an outer liner that acts as a cover for the liner component. Research on the contact pressure generated on the latest model of a dual-mobility hip joint prosthesis under a gait cycle has never been done before. The model is made of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) on the inner liner and 316L stainless steel (SS 316L) on the outer liner and acetabular cup. Simulation modeling using the finite element method is considered static loading with an implicit solver for studying the geometric parameter design of dual-mobility hip joint prostheses. In this study, simulation modeling was carried out by applying varying inclination angles of 30°, 40°, 45°, 50°, 60°, and 70° to the acetabular cup component. Three-dimensional loads were placed on femoral head reference points with variations of femoral head diameter used at 22 mm, 28 mm, and 32 mm. The results in the inner surface of the inner liner, the outer surface of the outer liner, and the inner surface of the acetabular cup showed that the variations in inclination angle do not have a major effect on the maximum contact pressure value on the liner component, where the acetabular cup with an inclination angle of 45° can reduce contact pressure more than the other studied inclination angle variations. In addition, it was found that the 22 mm diameter of the femoral head increases the contact pressure. The use of a larger diameter femoral head with an acetabular cup configuration at a 45° inclination can minimize the risk of implant failure due to wear.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of contact behavior on a model of the dual-mobility artificial hip joint for Asians in different inner liner thicknesses.World J Orthop. 2024 Apr 18;15(4):321-336. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i4.321. eCollection 2024 Apr 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38680676 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Cup Inclination Angle with Liner Wear for Metal-on-polyethylene in Hip Primary Arthroplasty.Orthop Surg. 2017 May;9(2):186-190. doi: 10.1111/os.12337. Epub 2017 May 30. Orthop Surg. 2017. PMID: 28557297 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of inclination and anteversion angles on kinematics and contact mechanics of dual mobility hip implants.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2018 Aug;57:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2018. PMID: 29933214
-
Effect of acetabular cup abduction angle on wear of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene in hip simulator testing.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014 Oct;43(10):466-71. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014. PMID: 25303445
-
Adopted walking condition for computational simulation approach on bearing of hip joint prosthesis: review over the past 30 years.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 5;8(12):e12050. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12050. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36506403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of Revision Hip Arthroplasty Workflow by Means of Detailed Pre-Surgical Planning Using Computed Tomography Data, Open-Source Software and Three-Dimensional-Printed Models.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;13(15):2516. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152516. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568878 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Regenerative Medicine: Applications and Implications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;8(5):442. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050442. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Strength, High-Water-Retention Hemicellulose-Based Hydrogel and Its Application in Urea Slow Release.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 24;24(11):9208. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119208. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298162 Free PMC article.
-
Wear Analysis of 3D-Printed Spur and Herringbone Gears Used in Automated Retail Kiosks Based on Computer Vision and Statistical Methods.Materials (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;16(16):5554. doi: 10.3390/ma16165554. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629844 Free PMC article.
-
Clustered Occurrence of Osteitis Condensans Ilii in Patients with Symptomatic Hip Dysplasia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 11;13(10):1701. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13101701. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eko S. The Tribological Behaviour of the Dual Mobility Hip Prosthesis in Relation to Impingement. University of Twente; 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

