Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics
- PMID: 36864178
- PMCID: PMC9979144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-023-00580-2
Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics
Abstract
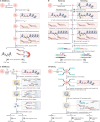
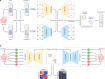
The joint analysis of the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome and/or metabolome from single cells is transforming our understanding of cell biology in health and disease. In less than a decade, the field has seen tremendous technological revolutions that enable crucial new insights into the interplay between intracellular and intercellular molecular mechanisms that govern development, physiology and pathogenesis. In this Review, we highlight advances in the fast-developing field of single-cell and spatial multi-omics technologies (also known as multimodal omics approaches), and the computational strategies needed to integrate information across these molecular layers. We demonstrate their impact on fundamental cell biology and translational research, discuss current challenges and provide an outlook to the future.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
T.V. is co-inventor on licensed patents WO/2011/157846 (Methods for haplotyping single cells), WO/2014/053664 (High-throughput genotyping by sequencing low amounts of genetic material) and WO/2015/028576 (Haplotyping and copy number typing using polymorphic variant allelic frequencies).
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

