Maternal and newborn plasma oxytocin levels in response to maternal synthetic oxytocin administration during labour, birth and postpartum - a systematic review with implications for the function of the oxytocinergic system
- PMID: 36864410
- PMCID: PMC9979579
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-05221-w
Maternal and newborn plasma oxytocin levels in response to maternal synthetic oxytocin administration during labour, birth and postpartum - a systematic review with implications for the function of the oxytocinergic system
Abstract
Background: The reproductive hormone oxytocin facilitates labour, birth and postpartum adaptations for women and newborns. Synthetic oxytocin is commonly given to induce or augment labour and to decrease postpartum bleeding.
Aim: To systematically review studies measuring plasma oxytocin levels in women and newborns following maternal administration of synthetic oxytocin during labour, birth and/or postpartum and to consider possible impacts on endogenous oxytocin and related systems.
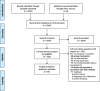
Methods: Systematic searches of PubMed, CINAHL, PsycInfo and Scopus databases followed PRISMA guidelines, including all peer-reviewed studies in languages understood by the authors. Thirty-five publications met inclusion criteria, including 1373 women and 148 newborns. Studies varied substantially in design and methodology, so classical meta-analysis was not possible. Therefore, results were categorized, analysed and summarised in text and tables.
Results: Infusions of synthetic oxytocin increased maternal plasma oxytocin levels dose-dependently; doubling the infusion rate approximately doubled oxytocin levels. Infusions below 10 milliunits per minute (mU/min) did not raise maternal oxytocin above the range observed in physiological labour. At high intrapartum infusion rates (up to 32 mU/min) maternal plasma oxytocin reached 2-3 times physiological levels. Postpartum synthetic oxytocin regimens used comparatively higher doses with shorter duration compared to labour, giving greater but transient maternal oxytocin elevations. Total postpartum dose was comparable to total intrapartum dose following vaginal birth, but post-caesarean dosages were higher. Newborn oxytocin levels were higher in the umbilical artery vs. umbilical vein, and both were higher than maternal plasma levels, implying substantial fetal oxytocin production in labour. Newborn oxytocin levels were not further elevated following maternal intrapartum synthetic oxytocin, suggesting that synthetic oxytocin at clinical doses does not cross from mother to fetus.
Conclusions: Synthetic oxytocin infusion during labour increased maternal plasma oxytocin levels 2-3-fold at the highest doses and was not associated with neonatal plasma oxytocin elevations. Therefore, direct effects from synthetic oxytocin transfer to maternal brain or fetus are unlikely. However, infusions of synthetic oxytocin in labour change uterine contraction patterns. This may influence uterine blood flow and maternal autonomic nervous system activity, potentially harming the fetus and increasing maternal pain and stress.
Keywords: Augmentation of labour; Induction of labour; Maternal oxytocin; Newborn oxytocin; Oxytocin; Pitocin; Postpartum oxytocin; Synthetic oxytocin; Syntocinon.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal plasma levels of oxytocin during physiological childbirth - a systematic review with implications for uterine contractions and central actions of oxytocin.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019 Aug 9;19(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2365-9. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019. PMID: 31399062 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology and pharmacology of oxytocin in labor and in the peripartum period.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Mar;230(3S):S740-S758. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.04.011. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38462255 Review.
-
Association of oxytocin augmentation and duration of labour with postpartum haemorrhage: A cohort study of nulliparous women.Midwifery. 2023 Aug;123:103705. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2023.103705. Epub 2023 May 9. Midwifery. 2023. PMID: 37244235 Clinical Trial.
-
Active management of the third stage of labour: prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009 Oct;31(10):980-993. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)34329-8. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009. PMID: 19941729 Review.
-
Striving for scientific stringency: a re-analysis of a randomised controlled trial considering first-time mothers' obstetric outcomes in relation to birth position.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012 Nov 22;12:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-12-135. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012. PMID: 23173988 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Uterine dynamics, blood profiles, and electronic fetal monitoring of primiparous and multiparous bitches classified according to their weight.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 16;10:1282389. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1282389. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38033635 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Maternal Oxytocin Induction during Birth on Early Neonatal Pain and Stress: A Quasi-Experimental Study.Biol Res Nurs. 2025 Jan;27(1):101-108. doi: 10.1177/10998004241289896. Epub 2024 Oct 6. Biol Res Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39370412 Free PMC article.
-
New policies on skin-to-skin contact warrant an oxytocin-based perspective on perinatal health care.Front Psychol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1385320. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1385320. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39049943 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin in growth, reproduction, restoration and health.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2024 Sep 30;20:100268. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2024.100268. eCollection 2024 Nov. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39435014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Close encounters with oxytocin.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023 Jun 29;15:100189. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2023.100189. eCollection 2023 Aug. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37577297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uvnäs-Moberg K, Ekström-Bergström A, Berg M, Buckley S, Pajalic Z, Hadjigeorgiou E, et al. Maternal plasma levels of oxytocin during physiological childbirth - a systematic review with implications for uterine contractions and central actions of oxytocin. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2365-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uvnas-Moberg K. Oxytocin: the biological guide to motherhood. Amarillo: Praeclarus Press; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

