Helical coiling of metaphase chromatids
- PMID: 36864547
- PMCID: PMC10085683
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad028
Helical coiling of metaphase chromatids
Abstract
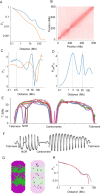
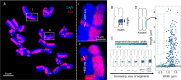
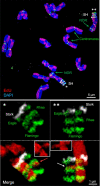
Chromatids of mitotic chromosomes were suggested to coil into a helix in early cytological studies and this assumption was recently supported by chromosome conformation capture (3C) sequencing. Still, direct differential visualization of a condensed chromatin fibre confirming the helical model was lacking. Here, we combined Hi-C analysis of purified metaphase chromosomes, biopolymer modelling and spatial structured illumination microscopy of large fluorescently labeled chromosome segments to reveal the chromonema - a helically-wound, 400 nm thick chromatin thread forming barley mitotic chromatids. Chromatin from adjacent turns of the helix intermingles due to the stochastic positioning of chromatin loops inside the chromonema. Helical turn size varies along chromosome length, correlating with chromatin density. Constraints on the observable dimensions of sister chromatid exchanges further supports the helical chromonema model.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Manton I. The spiral structure of chromosomes. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1950; 25:486–508. - PubMed
-
- Ohnuki Y. Structure of chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1968; 25:402–428. - PubMed
-
- Saitoh Y., Laemmli U.K.. Metaphase chromosome structure: bands arise from a differential folding path of the highly AT-rich scaffold. Cell. 1994; 76:609–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

