Stroke in hemodialysis patients and its association with CHA2DS2-VASC and HAS-BLED scores: a retrospective study
- PMID: 36865009
- PMCID: PMC9972838
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac260
Stroke in hemodialysis patients and its association with CHA2DS2-VASC and HAS-BLED scores: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: In the general population, the CHA2DS2-VASC and the HAS-BLED scores are helpful to predict cerebrovascular events and hemorrhage in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). However, their predictive value remains controversial in the dialysis population. This study aims to explore the association between these scores and cerebral cardiovascular events in hemodialysis (HD) patients.
Methods: This is a retrospective study including all HD patients treated between January 2010 and December 2019 in two Lebanese dialysis facilities. Exclusion criteria are patients younger than 18 years old and patients with a dialysis vintage less than 6 months.
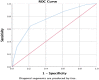
Results: A total of 256 patients were included (66.8% men; mean age 69.3 ± 13.9 years). The CHA2DS2-VASc score was significantly higher in patients with stroke (P = .043). Interestingly, this difference was significant in patients without AF (P = .017). Using receiver operating curve analysis, CHA2DS2-VASc score had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.628 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.539-0.718) and the best cut-off value for this score was 4. The HAS-BLED score was also significantly higher in patients with a hemorrhagic event (P < .001). AUC for HAS-BLED score was 0.756 (95% CI: 0.686-0.825) and the best cut-off value was also 4.
Conclusions: In HD patients, CHA2DS2-VASc score can be associated with stroke and HAS-BLED score can be associated with hemorrhagic events even in patients without AF. Patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥4 are at the highest risk for stroke and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, and those with a HAS-BLED score ≥4 are at the highest risk for bleeding.
Keywords: CHA2DS2-VASc; HAS-BLED; atrial fibrillation; chronic hemodialysis; stroke.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
References
-
- USRDS 2006 annual data report: atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: US Renal Data System, 2006n.d.
-
- Delanaye P, Bouquegneau A, Dubois Eet al. Fibrillation auriculaire et anticoagulation chez le patient hémodialysé: une decision difficile. Nephrol Ther 2017;13:9–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources