This is a preprint.
SPA-STOCSY: An Automated Tool for Identification of Annotated and Non-Annotated Metabolites in High-Throughput NMR Spectra
- PMID: 36865102
- PMCID: PMC9980041
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.02.22.529564
SPA-STOCSY: An Automated Tool for Identification of Annotated and Non-Annotated Metabolites in High-Throughput NMR Spectra
Update in
-
SPA-STOCSY: an automated tool for identifying annotated and non-annotated metabolites in high-throughput NMR spectra.Bioinformatics. 2023 Oct 3;39(10):btad593. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad593. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37792497 Free PMC article.
Abstract
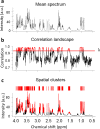
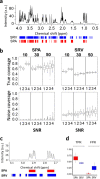
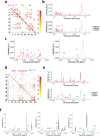
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is widely used to analyze metabolites in biological samples, but the analysis can be cumbersome and inaccurate. Here, we present a powerful automated tool, SPA-STOCSY (Spatial Clustering Algorithm - Statistical Total Correlation Spectroscopy), which overcomes the challenges by identifying metabolites in each sample with high accuracy. As a data-driven method, SPA-STOCSY estimates all parameters from the input dataset, first investigating the covariance pattern and then calculating the optimal threshold with which to cluster data points belonging to the same structural unit, i.e. metabolite. The generated clusters are then automatically linked to a compound library to identify candidates. To assess SPA-STOCSY’s efficiency and accuracy, we applied it to synthesized and real NMR data obtained from Drosophila melanogaster brains and human embryonic stem cells. In the synthesized spectra, SPA outperforms Statistical Recoupling of Variables, an existing method for clustering spectral peaks, by capturing a higher percentage of the signal regions and the close-to-zero noise regions. In the real spectra, SPA-STOCSY performs comparably to operator-based Chenomx analysis but avoids operator bias and performs the analyses in less than seven minutes of total computation time. Overall, SPA-STOCSY is a fast, accurate, and unbiased tool for untargeted analysis of metabolites in the NMR spectra. As such, it might accelerate the utilization of NMR for scientific discoveries, medical diagnostics, and patient-specific decision making.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
