This is a preprint.
Glutamine metabolism inhibition has dual immunomodulatory and antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 36865287
- PMCID: PMC9980128
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529704
Glutamine metabolism inhibition has dual immunomodulatory and antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Update in
-
Glutamine metabolism inhibition has dual immunomodulatory and antibacterial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 16;14(1):7427. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43304-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37973991 Free PMC article.
Abstract
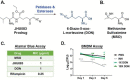
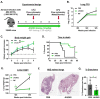
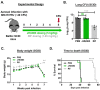
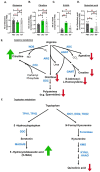
As one of the most successful human pathogens, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) has evolved a diverse array of determinants to subvert host immunity and alter host metabolic patterns. However, the mechanisms of pathogen interference with host metabolism remain poorly understood. Here we show that a novel glutamine metabolism antagonist, JHU083, inhibits Mtb proliferation in vitro and in vivo. JHU083-treated mice exhibit weight gain, improved survival, a 2.5 log lower lung bacillary burden at 35 days post-infection, and reduced lung pathology. JHU083 treatment also initiates earlier T-cell recruitment, increased proinflammatory myeloid cell infiltration, and a reduced frequency of immunosuppressive myeloid cells when compared to uninfected and rifampin-treated controls. Metabolomics analysis of lungs from JHU083-treated Mtb-infected mice revealed reduced glutamine levels, citrulline accumulation suggesting elevated NOS activity, and lowered levels of quinolinic acid which is derived from the immunosuppressive metabolite kynurenine. When tested in an immunocompromised mouse model of Mtb infection, JHU083 lost its therapeutic efficacy suggesting the drug's host-directed effects are likely to be predominant. Collectively, these data reveal that JHU083-mediated glutamine metabolism inhibition results in dual antibacterial and host-directed activity against tuberculosis.
Keywords: Glutamine inhibition; Host-directed therapy; Immunotherapy; TB drug; Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT SP, JS, SL, LZ, BK, JRM, BS and WRB declare no conflict of interest. RR, JDP. and BSS are inventors on multiple Johns Hopkins University (JHU) patents covering novel glutamine antagonist prodrugs including JHU083 and their utility. These patents have been licensed to Dracen Pharmaceuticals Inc. RR, JDP, and BSS are founders of and hold equity in Dracen Pharmaceuticals Inc. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the JHU in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. RDL is an inventor on US patent 10842763 submitted by Johns Hopkins University and licensed to Dracen Pharmaceuticals that covers the use of glutamine analogues, such as JHU083 (DRP-083), for cancer immunotherapy. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO (2022). Global tuberculosis report 2022.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
