Role of chemokine-like factor 1 as an inflammatory marker in diseases
- PMID: 36865551
- PMCID: PMC9971601
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1085154
Role of chemokine-like factor 1 as an inflammatory marker in diseases
Abstract
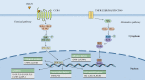
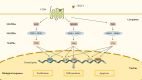
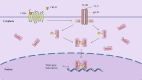
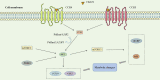
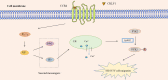
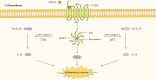
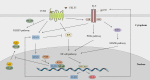
Immunoinflammatory mechanisms have been incrementally found to be involved in the pathogenesis of multiple diseases, with chemokines being the main drivers of immune cell infiltration in the inflammatory response. Chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1), a novel chemokine, is highly expressed in the human peripheral blood leukocytes and exerts broad-spectrum chemotactic and pro-proliferative effects by activating multiple downstream signaling pathways upon binding to its functional receptors. Furthermore, the relationship between CKLF1 overexpression and various systemic diseases has been demonstrated in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. In this context, it is promising that clarifying the downstream mechanism of CKLF1 and identifying its upstream regulatory sites can yield new strategies for targeted therapeutics of immunoinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: chemokine-like factor 1; immune-related disease; pathogenic mechanism; signaling pathways; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Yu and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CKLF1 in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 30;139:112718. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112718. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39032474 Review.
-
Chemokine-like factor-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family in autoimmune diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Apr 20;133(8):951-958. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000747. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 32195671 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine-like factor 1 (CLFK1) is over-expressed in patients with atopic dermatitis.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Aug 13;9(8):759-65. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6291. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23983609 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1) aggravates neointimal hyperplasia through activating the NF-κB /VCAM-1 pathway.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Sep;10(9):1880-1890. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12942. Epub 2020 Aug 14. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32741140 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in pharmacological research of chemokine like factor 1 (CKLF1).Cytokine. 2018 Feb;102:41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29275012 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 controls CKLF1-mediated apoptosis to reduce hypoxic/reoxygenation injury in HT22 cells.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 29;16:1525605. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1525605. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40365317 Free PMC article.
-
Research insights into the chemokine-like factor (CKLF)-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family (CMTM): their roles in various tumors.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 10;12:e16757. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16757. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38223763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individualized diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A rank-based qualitative T cell-related signature.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 26;20(6):e0326027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326027. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40569958 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of therapeutic response to statin drugs in cardiovascular disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 3;14(1):18005. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68665-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39097628 Free PMC article.
-
CKLF1 disrupts microglial efferocytosis following acute ischemic stroke by binding to phosphatidylserine.Cell Death Differ. 2025 Aug;32(8):1499-1517. doi: 10.1038/s41418-025-01475-x. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 40057593
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

