Clinical Validation of Siemens' Syngo.via Automatic Contouring System
- PMID: 36865668
- PMCID: PMC9972393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101177
Clinical Validation of Siemens' Syngo.via Automatic Contouring System
Abstract
Purpose: The manual delineation of organs at risk is a process that requires a great deal of time both for the technician and for the physician. Availability of validated software tools assisted by artificial intelligence would be of great benefit, as it would significantly improve the radiation therapy workflow, reducing the time required for segmentation. The purpose of this article is to validate the deep learning-based autocontouring solution integrated in syngo.via RT Image Suite VB40 (Siemens Healthineers, Forchheim, Germany).
Methods and materials: For this purpose, we have used our own specific qualitative classification system, RANK, to evaluate more than 600 contours corresponding to 18 different automatically delineated organs at risk. Computed tomography data sets of 95 different patients were included: 30 patients with lung, 30 patients with breast, and 35 male patients with pelvic cancer. The automatically generated structures were reviewed in the Eclipse Contouring module independently by 3 observers: an expert physician, an expert technician, and a junior physician.
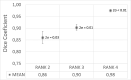
Results: There is a statistically significant difference between the Dice coefficient associated with RANK 4 compared with the coefficient associated with RANKs 2 and 3 (P < .001). In total, 64% of the evaluated structures received the maximum score, 4. Only 1% of the structures were classified with the lowest score, 1. The time savings for breast, thorax, and pelvis were 87.6%, 93.5%, and 82.2%, respectively.
Conclusions: Siemens' syngo.via RT Image Suite offers good autocontouring results and significant time savings.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Vinod SK, Jameson MG, Min M, Holloway LC. Uncertainties in volume delineation in radiation oncology: A systematic review and recommendations for future studies. Radiother Oncol. 2016;121:169–179. - PubMed
-
- Vinod SK, Min M, Jameson MG, Holloway LC. A review of interventions to reduce inter-observer variability in volume delineation in radiation oncology. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2016;60:393–406. - PubMed
-
- Wright JL, Yom SS, Awan MJ, et al. Standardizing normal tissue contouring for radiation therapy treatment planning: An ASTRO Consensus Paper. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019;9:65–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources