In vivo characterization and analysis of glioblastoma at different stages using multiscale photoacoustic molecular imaging
- PMID: 36865670
- PMCID: PMC9972568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100462
In vivo characterization and analysis of glioblastoma at different stages using multiscale photoacoustic molecular imaging
Abstract
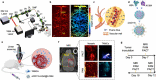
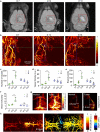
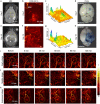
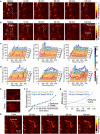
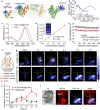
Simultaneous spatio-temporal description of tumor microvasculature, blood-brain barrier, and immune activity is pivotal to understanding the evolution mechanisms of highly aggressive glioblastoma, one of the most common primary brain tumors in adults. However, the existing intravital imaging modalities are still difficult to achieve it in one step. Here, we present a dual-scale multi-wavelength photoacoustic imaging approach cooperative with/without unique optical dyes to overcome this dilemma. Label-free photoacoustic imaging depicted the multiple heterogeneous features of neovascularization in tumor progression. In combination with classic Evans blue assay, the microelectromechanical system based photoacoustic microscopy enabled dynamic quantification of BBB dysfunction. Concurrently, using self-fabricated targeted protein probe (αCD11b-HSA@A1094) for tumor-associated myeloid cells, unparalleled imaging contrast of cells infiltration associated with tumor progression was visualized by differential photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window at dual scale. Our photoacoustic imaging approach has great potential for tumor-immune microenvironment visualization to systematically reveal the tumor infiltration, heterogeneity, and metastasis in intracranial tumors.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Brain tumor; Immune environment; Multiscale photoacoustic imaging; Vascular quantitative analysis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Li Y.M., Suki D., Hess K., Sawaya R. The influence of maximum safe resection of glioblastoma on survival in 1229 patients: Can we do better than gross-total resection? J. Neurosurg. 2016;124(4):977–988. - PubMed
-
- Wen P.Y., Reardon D.A. Neuro-oncology in 2015: progress in glioma diagnosis, classification and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016;12(2):69–70. - PubMed
-
- Norden A.D., Drappatz J., Wen P.Y. Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(12):1152–1160. - PubMed
-
- Osswald M., Blaes J., Liao Y., Solecki G., Gommel M., Berghoff A.S., Salphati L., Wallin J.J., Phillips H.S., Wick W., Winkler F. Impact of blood-brain barrier integrity on tumor growth and therapy response in brain metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22(24):6078–6087. - PubMed
-
- Sarkaria J.N., Hu L.S., Parney I.F., Pafundi D.H., Brinkmann D.H., Laack N.N., Giannini C., Burns T.C., Kizilbash S.H., Laramy J.K., Swanson K.R., Kaufmann T.J., Brown P.D., Agar N.Y.R., Galanis E., Buckner J.C., Elmquist W.F. Is the blood-brain barrier really disrupted in all glioblastomas? A critical assessment of existing clinical data. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(2):184–191. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

