Radiolabeled nanomaterial for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics: principles and concepts
- PMID: 36865684
- PMCID: PMC9968708
- DOI: 10.1186/s12645-023-00165-y
Radiolabeled nanomaterial for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics: principles and concepts
Abstract
In the last three decades, radiopharmaceuticals have proven their effectiveness for cancer diagnosis and therapy. In parallel, the advances in nanotechnology have fueled a plethora of applications in biology and medicine. A convergence of these disciplines has emerged more recently with the advent of nanotechnology-aided radiopharmaceuticals. Capitalizing on the unique physical and functional properties of nanoparticles, radiolabeled nanomaterials or nano-radiopharmaceuticals have the potential to enhance imaging and therapy of human diseases. This article provides an overview of various radionuclides used in diagnostic, therapeutic, and theranostic applications, radionuclide production through different techniques, conventional radionuclide delivery systems, and advancements in the delivery systems for nanomaterials. The review also provides insights into fundamental concepts necessary to improve currently available radionuclide agents and formulate new nano-radiopharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Cancer; Nano-radiopharmaceuticals; Nanotechnology; Radiolabeled nanomaterial; Radionuclides.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe author reports no competing interests in this work.
Figures
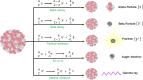




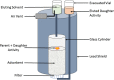

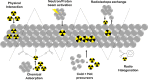

References
-
- Akca O, Unak P, Medine EI, Sakarya S, Kilcar AY, Ichedef C, Bekis R, Timur S. Radioiodine labeled CdSe/CdS quantum dots: lectin targeted dual probes. Radiochim Acta. 2014;102:849–859. doi: 10.1515/ract-2013-2152. - DOI
-
- Almutairi A, Rossin R, Shokeen M, Hagooly A, Ananth A, Capoccia B, Guillaudeu S, Abendschein D, Anderson CJ, Welch MJ, et al. Biodegradable dendritic positron-emitting nanoprobes for the noninvasive imaging of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:685–690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811757106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anarjan FS. Active targeting drug delivery nanocarriers: ligands. Nano Struct Nano Objects. 2019;19:100370. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100370. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
