An In Vivo Evaluation of Retention and Antibacterial Efficacy of Posterior High Strength Glass Ionomer Cement and Glass Hybrid Bulk-fill Alkasite Restorative Material as Conservative Adhesive Restoration in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Comparative Study
- PMID: 36865732
- PMCID: PMC9973112
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2435
An In Vivo Evaluation of Retention and Antibacterial Efficacy of Posterior High Strength Glass Ionomer Cement and Glass Hybrid Bulk-fill Alkasite Restorative Material as Conservative Adhesive Restoration in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Comparative Study
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the study was to compare and evaluate the retention and antibacterial efficacy of posterior high strength glass ionomer cement and glass hybrid bulk-fill alkasite restorative material as a conservative adhesive restoration in children with mixed dentition.
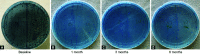
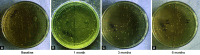
Materials and methods: A total of 60 children of age 6-12 years with mixed dentition were selected and divided into group I (control group n = 30): posterior high strength glass ionomer cement and group II (experimental group n = 30): glass hybrid bulk-fill alkasite restorative material. Restorative treatment was carried out using these two materials. Retention of the material and salivary Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus species count was estimated at baseline, 1, 3, and 6 months. The collected data were statistically analyzed using International Business Machines (IBM) Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software (version 20.0 Chicago, Illinois, USA).
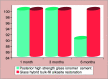
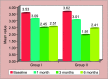
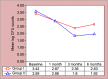
Results: About 100% retention of glass hybrid bulk-fill alkasite restorative material, and 90% retention of posterior high strength glass ionomer cement was observed according to United State Public Health Criteria. The * signifies statistically significant results, i.e. p < 0.0001 reduction in salivary S. mutans colony count and Lactobacillus species colony count was seen in both groups at different time intervals.
Conclusion: Both the materials showed good antibacterial properties, but glass hybrid bulk-fill alkasite restorative showed better retention, that is, 100% when compared to posterior high strength glass ionomer cement, which showed 90% retention at the end of 6 months follow-up.
How to cite this article: Soneta SP, Hugar SM, Hallikerimath S, et al. An In Vivo Evaluation of Retention and Antibacterial Efficacy of Posterior High Strength Glass Ionomer Cement and Glass Hybrid Bulk-fill Alkasite Restorative Material as Conservative Adhesive Restoration in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Comparative Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2022;15(5):529-534.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Children; Conservative adhesive restoration; Glass hybrid bulk-fill restorative material; Posterior high strength glass ionomer cement.
Copyright © 2022; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures


References
-
- Qin M, Liu HS. Clinical evaluation of a flowable resin composite and flowable compomer for preventive resin restorations. Oper Dent. 2005;30(5):580–587. - PubMed
-
- Cho SY, Cheng AC. A review of glass ionomer restorations in the primary dentition. J Can Dent Assoc. 1999;65(9):491–495. - PubMed
-
- Ivoclar Vivadent. Cention N (Scientific Documentation). Australia: Ivoclar Vivadent.; 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
