Energy expenditure, dietary intake and energy availability in female professional football players
- PMID: 36865769
- PMCID: PMC9972418
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001553
Energy expenditure, dietary intake and energy availability in female professional football players
Abstract
Objectives: To quantify energy expenditure and intake in professional female footballers playing on a national and/or international level. Second, to determine the prevalence of low energy availability among these players, defined as <30 kcal/kg fat-free mass (FFM)/day.
Methods: Fifty-one players completed a 14-day prospective observational study during the 2021/2022 football season. Energy expenditure was determined using the doubly labelled water method. Energy intake was assessed using dietary recalls, while global positioning system determined the external physiological load. Descriptive statistics, stratification and the correlation between explainable variables and outcomes were conducted to quantify the energetic demands.
Results: The mean energy expenditure for all players (22±4 years) was 2918±322 kcal. Mean energy intake was 2274±450 kcal, resulting in a discrepancy of ~22%. Carbohydrate intake was below the recommended guidelines on match day at 4.5±1.9 g/kg. The mean energy availability was 36.7±17.7 kcal/kg FFM/day on matchday and 37.9±11.7 kcal/kg FFM/day on training days, resulting in a prevalence of 36% and 23% for low energy availability during the observational period, respectively.
Conclusion: These elite female football players displayed moderate energy expenditure levels and failed to meet the recommended levels of carbohydrate intake. In conjunction with inadequate nutritional periodisation, this will likely hamper performance through inadequate muscle glycogen resynthesis. In addition, we found a considerable prevalence of low energy availability on match and training days.
Keywords: Carbohydrates; Energy expenditure; Female athlete triad; Football; Nutrition.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
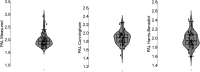
Similar articles
-
Energy expenditure and dietary intake in professional female football players in the Dutch Women's League: Implications for nutritional counselling.J Sports Sci. 2024 Feb;42(4):313-322. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2024.2329850. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Sports Sci. 2024. PMID: 38478743
-
Dietary Intake and Energy Expenditure Assessed during a Pre-Season Period in Elite Gaelic Football Players.Sports (Basel). 2019 Mar 13;7(3):62. doi: 10.3390/sports7030062. Sports (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30871227 Free PMC article.
-
Energy expenditure, intake and availability in female soccer players via doubly labelled water: Are we misrepresenting low energy availability?Exp Physiol. 2024 Aug 15. doi: 10.1113/EP091589. Online ahead of print. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39145767
-
Inside the Belly of a Beast: Individualizing Nutrition for Young, Professional Male Rugby League Players: A Review.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2021 Jan 1;31(1):73-89. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2019-0321. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2021. PMID: 33321472 Review.
-
Energy and carbohydrate for training and recovery.J Sports Sci. 2006 Jul;24(7):675-85. doi: 10.1080/02640410500482602. J Sports Sci. 2006. PMID: 16766497 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Carbohydrate Intake on Different Parameters of Soccer Players' Performance: Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 31;16(21):3731. doi: 10.3390/nu16213731. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519564 Free PMC article.
-
Risk for low energy availability, disordered eating and sleep disturbance among female football players.Phys Act Nutr. 2024 Sep;28(3):43-51. doi: 10.20463/pan.2024.0022. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Phys Act Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39501693 Free PMC article.
-
Low Energy Availability and Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2025 Feb;55(2):325-339. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02130-0. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 39485653
-
Evaluating the Suitability of the Low Energy Availability in Females Questionnaire (LEAF-Q) for Female Football Players.Sports Med Open. 2023 Jul 13;9(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40798-023-00605-4. Sports Med Open. 2023. PMID: 37439966 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional perspectives in female soccer: a scoping review.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024 Dec;21(1):2366427. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2366427. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38961627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scott D, Haigh J, Lovell R. Physical characteristics and match performances in women’s international versus domestic-level football players: a 2-year, league-wide study. Science and Medicine in Football 2020;4:211–5. 10.1080/24733938.2020.1745265 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
