A comprehensive overview of clinical research on dexmedetomidine in the past 2 decades: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36865921
- PMCID: PMC9971591
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1043956
A comprehensive overview of clinical research on dexmedetomidine in the past 2 decades: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
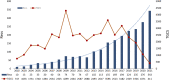
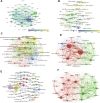
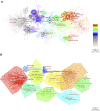
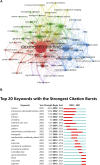
Introduction: Dexmedetomidine is a potent, highly selective α-2 adrenoceptor agonist with sedative, analgesic, anxiolytic, and opioid-sparing properties. A large number of dexmedetomidine-related publications have sprung out in the last 2 decades. However, no bibliometric analysis for clinical research on dexmedetomidine has been published to analyze hot spots, trends, and frontiers in this field. Methods: The clinical articles and reviews related to dexmedetomidine, published from 2002 to 2021 in the Web of Science Core Collection, were retrieved on 19 May 2022, using relevant search terms. VOSviewer and CiteSpace were used to conduct this bibliometric study. Results: The results showed that a total of 2,299 publications were retrieved from 656 academic journals with 48,549 co-cited references by 2,335 institutions from 65 countries/regions. The United States had the most publications among all the countries (n = 870, 37.8%) and the Harvard University contributed the most among all institutions (n = 57, 2.48%). The most productive academic journal on dexmedetomidine was Pediatric Anesthesia and the first co-cited journal was Anesthesiology. Mika Scheinin is the most productive author and Pratik P Pandharipande is the most co-cited author. Co-cited reference analysis and keyword analysis illustrated hot spots in the dexmedetomidine field including pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, intensive care unit sedation and outcome, pain management and nerve block, and premedication and use in children. The effect of dexmedetomidine sedation on the outcomes of critically ill patients, the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine, and its organ protective property are the frontiers in future research. Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis provided us with concise information about the development trend and provided an important reference for researchers to guide future research.
Keywords: Citespace; VOSviewer; bibliometric study; dexmedetomidine; sedation.
Copyright © 2023 Kong, Li, Deng, Wu, He and Mu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mapping Theme Trends and Research Frontiers in Dexmedetomidine Over Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 16;18:3043-3061. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S459431. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39050803 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and Frontiers of Research on Dexmedetomidine in Perioperative Medicine: A Bibliometric Analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 12;18:6017-6029. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S471602. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39687681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Articles on hemorrhagic shock published between 2000 and 2021: A CiteSpace-Based bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 7;9(8):e18840. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18840. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636355 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Endoscopic Sedation Research: 2001-2020.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 3;8:775495. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.775495. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35047526 Free PMC article.
-
Study on Pain Catastrophizing From 2010 to 2020: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Psychol. 2021 Dec 17;12:759347. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.759347. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34975649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine as a total intravenous anesthetic in pediatric patients undergoing cleft lip and palate surgery: a case series.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Jul 16;18(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04645-6. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39010154 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends and Global Collaborations in Anesthesia on Neuromuscular Blockers and Antagonists (2000-2024).Healthcare (Basel). 2025 May 14;13(10):1146. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13101146. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427982 Free PMC article.
-
Global research on sufentanil use in anesthesiology from 2003 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1412726. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412726. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39391693 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical adverse events to dexmedetomidine: a real-world drug safety study based on the FAERS database.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 2;15:1365706. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1365706. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39015372 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Brain Stimulation Technologies in Sleep Disorders.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Mar 5;30:e942687. doi: 10.12659/MSM.942687. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38439525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambesh S. P., Dubey M. (2021). Effect of intramuscular dexmedetomidine administration before extubation on post-extubation haemodynamics, postoperative sedation, and analgesic requirements: A double blind placebo controlled study. Asian J. Anesthesiol. 59 (3), 102–110. 10.6859/aja.202109_59(3).0004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buckley M. S., Smithburger P. L., Wong A., Fraser G. L., Reade M. C., Klein-Fedyshin M., et al. (2021). Dexmedetomidine for facilitating mechanical ventilation extubation in difficult-to-wean ICU patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. J. Intensive Care Med. 36 (8), 925–936. 10.1177/0885066620937673 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

