Dietary supplementation of Acanthopanax senticosus extract alleviates motor deficits in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice and its underlying mechanism
- PMID: 36865944
- PMCID: PMC9971719
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1121789
Dietary supplementation of Acanthopanax senticosus extract alleviates motor deficits in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice and its underlying mechanism
Abstract
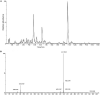
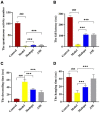
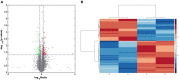
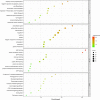
Acanthopanax senticosus extract (ASE), a dietary supplement with antifatigue, neuroprotective, and immunomodulatory properties, has been widely used due to its high polyphenol content. Our previous study showed that ASE could be used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD) as it contains multiple monoamine oxidase B inhibitors prescribed in early PD. However, its mechanism remains ambiguous. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of ASE on MPTP-induced PD in mice and explored the underlying mechanisms of action. We found that the administration of ASE significantly improved motor coordination in mice with MPTP-induced PD. As shown by quantitative proteomic analysis, 128 proteins' expression significantly changed in response to ASE administration, most of which were involved with Fcγ receptor-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages and monocytes signaling pathway, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and insulin receptor signaling pathway. Furthermore, the network analysis results showed that ASE modulates protein networks involved in regulating cellular assembly, lipid metabolism, and morphogenesis, all of which have implications for treating PD. Overall, ASE served as a potential therapeutic because it regulated multiple targets to improve motor deficits, which could lay the strong foundation for developing anti-PD dietary supplements.
Keywords: Acanthopanax senticosus extract; MPTP; Parkinson’s disease; proteomics; signaling pathway; therapeutic mechanism.
Copyright © 2023 Li, He, Fu, Wang, Fan, Zhong and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated proteomics and metabolomics reveals metabolism disorders in the α-syn mice and potential therapeutic effect of Acanthopanax senticosus extracts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116878. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116878. Epub 2023 Jul 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37419226
-
Cerebral metabonomics study on Parkinson's disease mice treated with extract of Acanthopanax senticosus harms.Phytomedicine. 2013 Oct 15;20(13):1219-29. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23830815
-
Acanthopanax senticosus Protects Structure and Function of Mesencephalic Mitochondria in A Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.Chin J Integr Med. 2018 Nov;24(11):835-843. doi: 10.1007/s11655-018-2935-5. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Chin J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 30090975
-
Quantitative proteomics analysis for effect of Acanthopanax senticosus extract on neuroinflammation.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan;28(1 Suppl):313-8. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25631509
-
Protective effect of extract of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms on dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease mice.Phytomedicine. 2012 May 15;19(7):631-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Phytomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22402244
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Enzymes Involved in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Aβ1-40 Aggregation by Citrus limon Peel Polyphenol Extract.Molecules. 2023 Aug 30;28(17):6332. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176332. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687161 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products and Their Neuroprotective Effects in Degenerative Brain Diseases: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 18;25(20):11223. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011223. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the extraction and purification methods, biological activities, and applications of active compounds in Acanthopanax senticosus.Front Nutr. 2024 May 23;11:1391601. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1391601. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38846546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Plant-Based Bioactive Compounds as Therapeutics in Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Nov 14;28(22):7588. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227588. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38005310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition and In Vitro Biological Activity of the Polar and Non-Polar Fractions Obtained from the Roots of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. et Maxim.) Maxim.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 12;26(12):5619. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125619. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565083 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

