Can the use of magnetized water affect the seedling development and the metabolite profiles of two different species: Lentil and durum wheat?
- PMID: 36865947
- PMCID: PMC9971934
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1066088
Can the use of magnetized water affect the seedling development and the metabolite profiles of two different species: Lentil and durum wheat?
Abstract
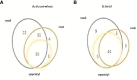
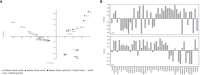
Seedlings of durum wheat and lentil were utilized to investigate the efficiency of magnetic water on growth and metabolic epicotyl profile. Tap water was passed through a magnetic device with a flow rate of max. 12900 - 13200 Gauss (G). Seeds and plantlets were grown on sand-free paper soaked by magnetized water, with unmagnetized tap water used in a control group. The growth parameters were collected at three time points (48, 96, and 144 hours after treatment), the same times at which metabolomic analysis was conducted on seeds, roots, and epicotyls. Although the effects varied with the species, tissues, and time point considered, compared with tap water (TW), the use of magnetized water treatment (MWT) led to higher root elongation in both genotypes. On the contrary, epicotyl length was not affected by treatment both in durum wheat and lentil. The results indicate that the use of magnetized water in agriculture can be considered a sustainable technology to promote plant development and quality with reduced and more efficient water usage, leading to cost-saving and environmental protection.
Keywords: magnetic device; plant growth; plant metabolites; sustainability; water use efficiency.
Copyright © 2023 Sestili, Platani, Palma, Dattoli and Beleggia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abd-Elrahman S. H., Shalaby O. A. (2017). Response of wheat plants to irrigation with magnetized water under Egyptian soil conditions. Egypt J. Soil Sci. 57 (4), 477–488. doi: 10.21608/ejss.2017.1605.1122 - DOI
-
- Abdollahi F., Amiri H., Niknam V., Ghanati F., Mahdigholi K. (2019). Effects of static magnetic fields on the antioxidant system of almond seeds. Russian J. Plant Physiol. 66 (2), 299–307. doi: 10.1134/S102144371902002X - DOI
-
- Akrimi R., Hajlaoui H., Batelli G., Ruggiero A., Mounawer B., Grillo S., et al. . (2021). Electromagnetic water enhanced metabolism and agro-physiological responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum l.) under saline conditions. J. Agro Crop Sci. 207, 44–58. doi: 10.1111/jac.12449 - DOI
-
- Alattar E., Alwasife K., Radwan E. (2020). Effects of treated water with neodymium magnets (NdFeB) on growth characteristics of pepper (Capsicum annuum). AIMS Biophys. 7 (4), 291–307. doi: 10.3934/biophy.2020021 - DOI
-
- Al-Bahrani H. S. (2018). Detecting and monitoring the magnetic effect in salty water via remote sensing technology using AQUA device. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 454, 12024. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/454/1/012024 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

