Whole-genome sequencing and phylogenomic analyses of a novel zearalenone-degrading Bacillus subtilis B72
- PMID: 36866327
- PMCID: PMC9971418
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03517-y
Whole-genome sequencing and phylogenomic analyses of a novel zearalenone-degrading Bacillus subtilis B72
Abstract
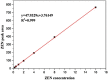
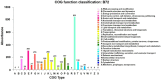
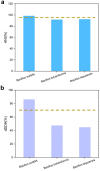
Bacillus strain B72 was previously isolated as a novel zearalenone (ZEN) degradation strain from the oil field soil in Xinjiang, China. The genome of B72 was sequenced with a 400 bp paired-end using the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform. De novo genome assembly was performed using SOAPdenovo2 assemblers. Phylogenetic analysis using 16S rRNA gene sequencing demonstrated that B72 is closely related to the novel Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) strain DSM 10. A phylogenetic tree based on 31 housekeeping genes, constructed with 19 strains closest at the species level, showed that B72 was closely related to B. subtilis 168, B. licheniformis PT-9, and B. tequilensis KCTC 13622. Detailed phylogenomic analysis using average nucleotide identity (ANI) and genome-to-genome distance calculator (GGDC) demonstrated that B72 might be classified as a novel B. subtilis strain. Our study demonstrated that B72 could degrade 100% of ZEN in minimal medium after 8 h of incubation, which makes it the fastest degrading strain to date. Moreover, we confirmed that ZEN degradation by B72 might involve degrading enzymes produced during the initial period of bacterial growth. Subsequently, functional genome annotation revealed that the laccase-encoding genes yfiH (gene 1743) and cotA (gene 2671) might be related to ZEN degradation in B72. The genome sequence of B. subtilis B72 reported here will provide a reference for genomic research on ZEN degradation in the field of food and feed.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03517-y.
Keywords: Bacillus sp.; Degradation; Mycotoxin; ZEN-degrading enzyme; Zearalenone.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Whole genome sequencing and phylogenomic analyses of a novel glufosinate-tolerant Pseudomonas species.3 Biotech. 2022 May;12(5):123. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03185-4. Epub 2022 Apr 25. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35547011 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation of ZEN by Bacillus mojavensis L-4: analysis of degradation conditions, products, degrading enzymes, and whole-genome sequencing, and its application in semi-solid-state fermentation of contaminated cornmeal.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1512781. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1512781. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40207149 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 2;15(8):488. doi: 10.3390/toxins15080488. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37624245 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in bio-degradation of mycotoxin zearalenone].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018 Apr 25;34(4):489-500. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170337. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 29701023 Review. Chinese.
-
Microbial and enzymatic battle with food contaminant zearalenone (ZEN).Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(12):4353-4365. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12009-7. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35705747 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycotoxin Biodegradation by Bacillus Bacteria-A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;16(11):478. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110478. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Bacillus subtilis: A Comprehensive Study on Mycotoxin Decontamination, Mechanistic Insights, and Efficacy Assessment in a Liquid Food Model.Foods. 2025 Jan 22;14(3):360. doi: 10.3390/foods14030360. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39941953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaurasia PK, Bharati SL, Sharma M, Singh SK, Yadav RSS, Yadava S. Fungal laccases and their biotechnological significances in the current perspective: a review. Curr Org Chem. 2015;19(19):1916–1934.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

