M13 phage: a versatile building block for a highly specific analysis platform
- PMID: 36867197
- PMCID: PMC9982796
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-023-04606-w
M13 phage: a versatile building block for a highly specific analysis platform
Abstract
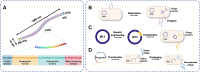
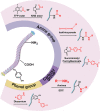
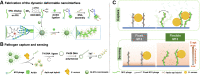
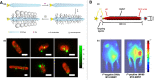
Viruses are changing the biosensing and biomedicine landscape due to their multivalency, orthogonal reactivities, and responsiveness to genetic modifications. As the most extensively studied phage model for constructing a phage display library, M13 phage has received much research attention as building blocks or viral scaffolds for various applications including isolation/separation, sensing/probing, and in vivo imaging. Through genetic engineering and chemical modification, M13 phages can be functionalized into a multifunctional analysis platform with various functional regions conducting their functionality without mutual disturbance. Its unique filamentous morphology and flexibility also promoted the analytical performance in terms of target affinity and signal amplification. In this review, we mainly focused on the application of M13 phage in the analytical field and the benefit it brings. We also introduced several genetic engineering and chemical modification approaches for endowing M13 with various functionalities, and summarized some representative applications using M13 phages to construct isolation sorbents, biosensors, cell imaging probes, and immunoassays. Finally, current issues and challenges remaining in this field were discussed and future perspectives were also proposed.
Keywords: Bioimaging; Biosensors; Immunoassays/ELISA; M13 phage; Phage display.
© 2023. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of the Magnetic Orientation of M13 Bacteriophage on Phage Display Selection.Chemistry. 2023 Nov 13;29(63):e202302261. doi: 10.1002/chem.202302261. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 37638672
-
Efficient affinity-tagging of M13 phage capsid protein IX for immobilization of protein III-displayed oligopeptide probes on abiotic platforms.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;104(3):1201-1209. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10338-8. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31900564
-
Preparation of Bioconjugates of Chimeric M13 Phage and Gold Nanorods.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2793:131-141. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3798-2_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38526728 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances of development of phage display systems].Yi Chuan. 2011 Oct;33(10):1113-20. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.01113. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 21993286 Review. Chinese.
-
Unraveling the potential of M13 phages in biomedicine: Advancing drug nanodelivery and gene therapy.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 1;238(Pt 1):117132. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117132. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37714365 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Phage-Displayed Nanobody-Based Competitive Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of Soybean Agglutinin.Foods. 2024 Jun 16;13(12):1893. doi: 10.3390/foods13121893. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928834 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico-Ex Vitro Iteration Strategy for Affinity Maturation of Anti-Ricin Peptides and the SPR Biosensing Application.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;15(8):490. doi: 10.3390/toxins15080490. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37624247 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-based delivery systems: engineering, applications, and challenges in nanomedicines.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 25;22(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02576-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38918839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances and Mechanisms of Phage-Based Therapies in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9938. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189938. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A modular phage vector platform for targeted photodynamic therapy of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens.iScience. 2023 Sep 27;26(10):108032. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108032. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37822492 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

