Australian Genomics: Outcomes of a 5-year national program to accelerate the integration of genomics in healthcare
- PMID: 36868206
- PMCID: PMC10027474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.01.018
Australian Genomics: Outcomes of a 5-year national program to accelerate the integration of genomics in healthcare
Abstract
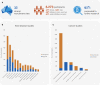
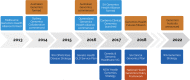
Australian Genomics is a national collaborative partnership of more than 100 organizations piloting a whole-of-system approach to integrating genomics into healthcare, based on federation principles. In the first five years of operation, Australian Genomics has evaluated the outcomes of genomic testing in more than 5,200 individuals across 19 rare disease and cancer flagship studies. Comprehensive analyses of the health economic, policy, ethical, legal, implementation and workforce implications of incorporating genomics in the Australian context have informed evidence-based change in policy and practice, resulting in national government funding and equity of access for a range of genomic tests. Simultaneously, Australian Genomics has built national skills, infrastructure, policy, and data resources to enable effective data sharing to drive discovery research and support improvements in clinical genomic delivery.
Copyright © 2023 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.L.W. is the Chair of the Medical Services Advisory Committee; the views in this paper are not representing those of the Commonwealth of Australia. I.E.S. has served on scientific advisory boards for BioMarin, Chiesi, Eisai, Encoded Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Knopp Biosciences, Nutricia, Rogcon, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Xenon Pharmaceuticals; has received speaker honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline, UCB, BioMarin, Biocodex, Chiesi, Liva Nova, Nutricia, Zuellig Pharma, and Eisai; has received funding for travel from UCB, Biocodex, GlaxoSmithKline, Biomarin, and Eisai; has served as an investigator for Anavex Life Sciences, Cerecin Inc, Cerevel Therapeutics, Eisai, Encoded Therapeutics, EpiMinder Inc, Epygenyx, ES-Therapeutics, GW Pharma, Marinus, Neurocrine BioSciences, Ovid Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Ultragenyx, Xenon Pharmaceuticals, Zogenix, and Zynerba; and has consulted for Care Beyond Diagnosis, Epilepsy Consortium, Atheneum Partners, Ovid Therapeutics, UCB, Zynerba Pharmaceuticals, BioMarin, Encoded Therapeutics, and Biohaven Pharmaceuticals; and is a Non-Executive Director of Bellberry Ltd and a Director of the Australian Academy of Health and Medical Sciences and the Australian Council of Learned Academies Limited. She may accrue future revenue on pending patent WO61/010,176 (filed: 2008): Therapeutic Compound; has a patent for SCN1A testing held by Bionomics Inc and licensed to various diagnostic companies; and has a patent molecular diagnostic/theranostic target for benign familial infantile epilepsy (BFIE) (PRRT2) 2,011,904,493 & 2,012,900,190 and PCT/AU2012/001,321 (TECH ID:2012-009).
Figures
References
-
- Turnbull C., Scott R.H., Thomas E., Jones L., Murugaesu N., Pretty F.B., Halai D., Baple E., Craig C., Hamblin A., et al. The 100 000 Genomes Project: bringing whole genome sequencing to the NHS. BMJ. 2018;361:k1687. - PubMed
-
- Fatumo S., Yakubu A., Oyedele O., Popoola J., Attipoe D.A., Eze-Echesi G., Modibbo F.Z., Ado-Wanka N., et al. 54gene Team. NCD-GHS Consortium Promoting the genomic revolution in Africa through the Nigerian 100K Genome Project. Nat. Genet. 2022;54:531–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

