KDM4A, involved in the inflammatory and oxidative stress caused by traumatic brain injury-hemorrhagic shock, partly through the regulation of the microglia M1 polarization
- PMID: 36869312
- PMCID: PMC9983262
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-023-00784-6
KDM4A, involved in the inflammatory and oxidative stress caused by traumatic brain injury-hemorrhagic shock, partly through the regulation of the microglia M1 polarization
Abstract
Background: Microglial polarization and the subsequent neuroinflammatory response and oxidative stress are contributing factors for traumatic brain injury (TBI) plus hemorrhagic shock (HS) induced brain injury. In the present work, we have explored whether Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 4 A (KDM4A) modulates microglia M1 polarization in the TBI and HS mice.
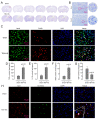
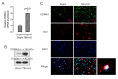
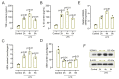
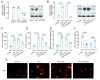
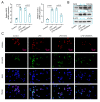
Results: Male C57BL/6J mice were used to investigate the microglia polarization in the TBI + HS model in vivo. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced BV2 cells were used to examine the mechanism of KDM4A in regulating microglia polarization in vitro. We found that TBI + HS resulted in neuronal loss and microglia M1 polarization in vivo, reflected by the increased level of Iba1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, malondialdehyde (MDA) and the decreased level of reduced glutathione (GSH). Additionally, KDM4A was upregulated in response to TBI + HS and microglia were among the cell types showing the increased level of KDM4A. Similar to the results in vivo, KDM4A also highly expressed in LPS-induced BV2 cells. LPS-induced BV2 cells exhibited enhanced microglia M1 polarization, and enhanced level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS), while this enhancement was abolished by the suppression of KDM4A.
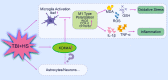
Conclusion: Accordingly, our findings indicated that KDM4A was upregulated in response to TBI + HS and microglia were among the cell types showing the increased level of KDM4A. The important role of KDM4A in TBI + HS-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress was at least partially realized through regulating microglia M1 polarization.
Keywords: HS; KDM4A; M1 polarization; Microglia; TBI.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid attenuates the inflammatory response by modulating microglia polarization through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of the HMGB1/NF-κB pathway following experimental traumatic brain injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Apr 20;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1151-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29678169 Free PMC article.
-
CD36 deletion prevents white matter injury by modulating microglia polarization through the Traf5-MAPK signal pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jun 5;21(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03143-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38840180 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylase KDM4A mediating macrophage polarization: A potential mechanism of trichloroethylene induced liver injury.Cell Biol Int. 2024 Aug;48(8):1148-1159. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12187. Epub 2024 May 27. Cell Biol Int. 2024. PMID: 38800986
-
Microglial polarization in TBI: Signaling pathways and influencing pharmaceuticals.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Aug 1;14:901117. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.901117. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35978950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Contributions to Recovery following Brain Trauma: A Narrative Review.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Mar 15;29(3):103. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2903103. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38538271 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of KDM4A in Regulating Microglial Polarization in Ischemic Stroke.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;197(6):3871-3889. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05207-2. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40080374
-
UCF-101 ameliorates traumatic brain injury by promoting microglia M2 polarization via AMPK/NF-κB pathways in LPS-induced BV2 cells.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 30;56(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10336-9. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39739143
-
Recent Advances and Therapeutic Implications of 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases in Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):3949-3975. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03790-1. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38041714 Review.
-
Circular RNA KIAA0564 Serves as a Competitive Endogenous RNA for MicroRNA-424-5p, Mediating the Expression of Lysine Demethylase 4a, Thereby Facilitating Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;196(11):8134-8155. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04962-y. Epub 2024 May 1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38691277
References
-
- Rhind SG, Crnko NT, Baker AJ, Morrison LJ, Shek PN, Scarpelini S, Rizoli SB. Prehospital resuscitation with hypertonic saline-dextran modulates inflammatory, coagulation and endothelial activation marker profiles in severe traumatic brain injured patients. J Neuroinflamm. 2010;7:5. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nikolian VC, Dekker SE, Bambakidis T, Higgins GA, Dennahy IS, Georgoff PE, Williams AM, Andjelkovic AV, Alam HB. Improvement of blood-brain Barrier Integrity in Traumatic Brain Injury and hemorrhagic shock following treatment with Valproic Acid and Fresh Frozen plasma. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(1):e59–e66. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002800. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

