A Novel In Vitro Assay Correlates Insulin Receptor Autoantibodies With Fasting Insulin in Type B Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 36869714
- PMCID: PMC10438904
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgad125
A Novel In Vitro Assay Correlates Insulin Receptor Autoantibodies With Fasting Insulin in Type B Insulin Resistance
Abstract
Context: Severe insulin resistance (IR) in the presence of insulin receptor autoantibodies (InsR-aAb) is known as type B insulin resistance (TBIR). Considerable progress in therapy has been achieved, but diagnosis and monitoring of InsR-aAb remains a challenge.
Objective: This work aimed to establish a robust in vitro method for InsR-Ab quantification.
Methods: Longitudinal serum samples from patients with TBIR at the National Institutes of Health were collected. A bridge-assay for InsR-aAb detection was established using recombinant human insulin receptor as bait and detector. Monoclonal antibodies served as positive controls for validation.
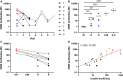
Results: The novel assay proved sensitive, robust, and passed quality control. The measured InsR-aAb from TBIR patients was associated with disease severity, decreased on treatment, and inhibited insulin signaling in vitro. Titers of InsR-aAb correlated positively to fasting insulin in patients.
Conclusion: Quantification of InsR-aAb from serum samples via the novel in vitro assay enables identification of TBIR and monitoring of successful therapy.
Keywords: acanthosis nigricans; assays; hyperglycemia; hypoglycemia; in vitro diagnostics; uncontrolled diabetes.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2023.
Figures


References
-
- Rodriguez O, Collier E, Arakaki R, Gorden P. Characterization of purified autoantibodies to the insulin receptor from six patients with type B insulin resistance. Metabolism. 1992;41(3):325‐331. - PubMed
-
- Musso C, Cochran E, Moran SA, et al. Clinical course of genetic diseases of the insulin receptor (type A and Rabson-Mendenhall syndromes): a 30-year prospective. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;83(4):209‐222. - PubMed
-
- Lupsa BC, Chong AY, Cochran EK, Soos MA, Semple RK, Gorden P. Autoimmune forms of hypoglycemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009;88(3):141‐153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

