A point mutation in the kinase domain of CRK10 leads to xylem vessel collapse and activation of defence responses in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 36869735
- PMCID: PMC10199123
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad080
A point mutation in the kinase domain of CRK10 leads to xylem vessel collapse and activation of defence responses in Arabidopsis
Abstract
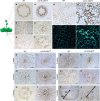
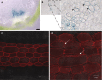
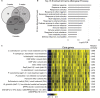
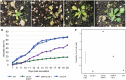
Cysteine-rich receptor-like kinases (CRKs) are a large family of plasma membrane-bound receptors ubiquitous in higher plants. However, despite their prominence, their biological roles have remained largely elusive so far. In this study we report the characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant named crk10-A397T in which alanine 397 has been replaced by a threonine in the αC helix of the kinase domain of CRK10, known to be a crucial regulatory module in mammalian kinases. The crk10-A397T mutant is a dwarf that displays collapsed xylem vessels in the root and hypocotyl, whereas the vasculature of the inflorescence develops normally. In situ phosphorylation assays with His-tagged wild type and crk10-A397T versions of the CRK10 kinase domain revealed that both alleles are active kinases capable of autophosphorylation, with the newly introduced threonine acting as an additional phosphorylation site in crk10-A397T. Transcriptomic analysis of wild type and crk10-A397T mutant hypocotyls revealed that biotic and abiotic stress-responsive genes are constitutively up-regulated in the mutant, and a root-infection assay with the vascular pathogen Fusarium oxysporum demonstrated that the mutant has enhanced resistance to this pathogen compared with wild type plants. Taken together our results suggest that crk10-A397T is a gain-of-function allele of CRK10, the first such mutant to have been identified for a CRK in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: Fusarium oxysporum; Arabidopsis; cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase CRK10; defence response; gain-of-function mutation; kinase regulation; transcriptomics; xylem vessel collapse; αC helix.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Acharya BR, Raina S, Maqbool SB, Jagadeeswaran G, Mosher SL, Appel HM, Schultz JC, Klessig DF, Raina R.. 2007. Overexpression of CRK13, an Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase, results in enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae. The Plant Journal 50, 488–499. - PubMed
-
- Ahuja I, Kissen R, Bones AM.. 2012. Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends in Plant Sciences 17, 73–90. - PubMed
-
- Bacete L, Melida H, Miedes E, Molina A.. 2018. Plant cell wall-mediated immunity: cell wall changes trigger disease resistance responses. The Plant Journal 93, 614–636. - PubMed
-
- Beenstock J, Mooshayef N, Engelberg D.. 2016. How do protein kinases take a selfie (autophosphorylate)? Trends in Biochemical Sciences 41, 938–953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

