A Bayesian Network Approach to Social and Nonsocial Cognition in Schizophrenia: Are Some Domains More Fundamental than Others?
- PMID: 36869810
- PMCID: PMC10318874
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbad012
A Bayesian Network Approach to Social and Nonsocial Cognition in Schizophrenia: Are Some Domains More Fundamental than Others?
Abstract
Objectives: Social and nonsocial cognition are defined as distinct yet related constructs. However, the relative independence of individual variables-and whether specific tasks directly depend on performance in other tasks-is still unclear. The current study aimed to answer this question by using a Bayesian network approach to explore directional dependencies among social and nonsocial cognitive domains.
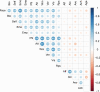
Study design: The study sample comprised 173 participants with schizophrenia (71.7% male; 28.3% female). Participants completed 5 social cognitive tasks and the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery. We estimated Bayesian networks using directed acyclic graph structures to examine directional dependencies among the variables.
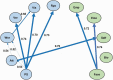
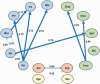
Study results: After accounting for negative symptoms and demographic variables, including age and sex, all nonsocial cognitive variables depended on processing speed. More specifically, attention, verbal memory, and reasoning and problem solving solely depended on processing speed, while a causal chain emerged between processing speed and visual memory (processing speed → attention → working memory → visual memory). Social processing variables within social cognition, including emotion in biological motion and empathic accuracy, depended on facial affect identification.
Conclusions: These results suggest that processing speed and facial affect identification are fundamental domains of nonsocial and social cognition, respectively. We outline how these findings could potentially help guide specific interventions that aim to improve social and nonsocial cognition in people with schizophrenia.
Keywords: DAG; facial affect; negative symptoms; processing speed; psychosis.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center 2023.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social and nonsocial cognition in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: relative levels of impairment.Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Mar;170(3):334-41. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12040490. Am J Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23450289 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive and psychomotor effects of risperidone in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.Clin Ther. 2008 Sep;30(9):1565-89. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.09.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18840365 Review.
-
Nonsocial cognitive underpinnings of theory of mind in schizophrenia.Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jul;289:113055. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113055. Epub 2020 May 15. Psychiatry Res. 2020. PMID: 32446008
-
Using the MATRICS to guide development of a preclinical cognitive test battery for research in schizophrenia.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 May;122(2):150-202. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.02.004. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19269307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of impaired processing speed on cognition in first-episode antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenic patients.Eur Psychiatry. 2013 Aug;28(6):332-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Eur Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22999439
Cited by
-
Individual-level deviations from normative brain morphology in violence, psychosis, and psychopathy.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 2;15(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03343-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40175325 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the interplay between psychopathological symptoms, sensorimotor, cognitive and global functioning: a transdiagnostic network analysis.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Oct;274(7):1625-1637. doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01782-3. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38509230 Free PMC article.
-
International Experience of Implementing Cognitive Remediation for People With Psychotic Disorders.Schizophr Bull. 2024 Aug 27;50(5):1017-1027. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbae071. Schizophr Bull. 2024. PMID: 38758086 Free PMC article.
-
Schizotypal Traits, Psychopathology, and Reflective Functioning Impairments During Adolescence: A Bayesian Network Approach.Schizophr Bull. 2025 Mar 4;51(Suppl 2):S214-S225. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbae041. Schizophr Bull. 2025. PMID: 40037827 Free PMC article.
-
Constructs across a hierarchical, dimensional model of psychopathology show differential associations with social and general cognitive ability.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 22;20(1):e0317377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317377. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39841648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green MF. Impact of cognitive and social cognitive impairment on functional outcomes in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016;77(Suppl 2):8–11. - PubMed
-
- Hoe M, Nakagami E, Green MF, Brekke JS.. The causal relationships between neurocognition, social cognition and functional outcome over time in schizophrenia: a latent difference score approach. Psychol Med. 2012;42(11):2287–2299. - PubMed

