Positive Impact of [18F]FDG-PET/CT on Mortality in Patients With Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Explained by Immortal Time Bias
- PMID: 36869816
- PMCID: PMC10320066
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciad112
Positive Impact of [18F]FDG-PET/CT on Mortality in Patients With Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Explained by Immortal Time Bias
Abstract
Background: Several studies have suggested that in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography ([18F]FDG-PET/CT) improves outcome. However, these studies often ignored possible immortal time bias.
Methods: Prospective multicenter cohort study in 2 university and 5 non-university hospitals, including all patients with SAB. [18F]FDG-PET/CT was performed on clinical indication as part of usual care. Primary outcome was 90-day all-cause mortality. Effect of [18F]FDG-PET/CT was modeled with a Cox proportional hazards model using [18F]FDG-PET/CT as a time-varying variable and corrected for confounders for mortality (age, Charlson score, positive follow-up cultures, septic shock, and endocarditis). Secondary outcome was 90-day infection-related mortality (assessed by adjudication committee) using the same analysis. In a subgroup-analysis, we determined the effect of [18F]FDG-PET/CT in patients with high risk of metastatic infection.
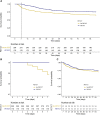
Results: Of 476 patients, 178 (37%) underwent [18F]FDG-PET/CT. Day-90 all-cause mortality was 31% (147 patients), and infection-related mortality was 17% (83 patients). The confounder adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for all-cause mortality was 0.50 (95% confidence interval [CI]: .34-.74) in patients that underwent [18F]FDG-PET/CT. Adjustment for immortal time bias changed the aHR to 1.00 (95% CI .68-1.48). Likewise, after correction for immortal time bias, [18F]FDG-PET/CT had no effect on infection-related mortality (cause specific aHR 1.30 [95% CI .77-2.21]), on all-cause mortality in patients with high-risk SAB (aHR 1.07 (95% CI .63-1.83) or on infection-related mortality in high-risk SAB (aHR for 1.24 [95% CI .67-2.28]).
Conclusions: After adjustment for immortal time bias [18F]FDG-PET/CT was not associated with day-90 all-cause or infection-related mortality in patients with SAB.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia; [18F]FDG-PET/CT; immortal time bias; mortality.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. M. J. B. reports funding through grants or contracts to the author's institution from Janssen Vaccines, Novaritis, CureVac, and Merck; payment or honoraria made to the author from Takeda; and participation on a Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Board for Sanofi, Spherecydes, Pfizer, Merck, Novartis, and Astra-Zeneca for unrelated works. C. H. W. reports funding through grants or contracts from DaVolterra, bioMérieux, and LimmaTech, as well as consulting fees from Merck/MSD and Sanofi-Pasteur for unrelated works, all of which were paid to the author's institution. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

Comment in
-
Positron Emission Tomography in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: Peeking Under the Covers.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 5;77(1):16-18. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad113. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36869804 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berrevoets MAH, Kouijzer IJE, Aarntzen E, et al. . [18F]FDG PET/CT optimizes treatment in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and is associated with reduced mortality. J Nucl Med 2017; 58:1504–10. - PubMed
-
- Ghanem-Zoubi N, Kagna O, Abu-Elhija J, et al. . Integration of FDG-PET/CT in the diagnostic workup for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a prospective interventional matched-cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2021; 73:e3859–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

