Flavonols modulate plant development, signaling, and stress responses
- PMID: 36870100
- PMCID: PMC10372886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2023.102350
Flavonols modulate plant development, signaling, and stress responses
Abstract
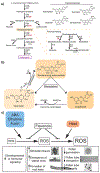
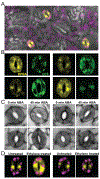
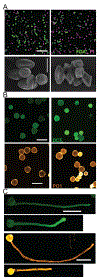
Flavonols are plant-specialized metabolites with important functions in plant growth and development. Isolation and characterization of mutants with reduced flavonol levels, especially the transparent testa mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana, have contributed to our understanding of the flavonol biosynthetic pathway. These mutants have also uncovered the roles of flavonols in controlling development in above- and below-ground tissues, notably in the regulation of root architecture, guard cell signaling, and pollen development. In this review, we present recent progress made towards a mechanistic understanding of flavonol function in plant growth and development. Specifically, we highlight findings that flavonols act as reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavengers and inhibitors of auxin transport in diverse tissues and cell types to modulate plant growth and development and responses to abiotic stresses.
Keywords: Flavonoids; Flavonols; Pollen development; Reactive oxygen species; Root development; Stomatal closure.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Gayomba SR, Watkins JM, Muday GK: Flavonols Regulate Plant Growth and Development through Regulation of Auxin Transport and Cellular Redox Status. In Recent Advances in Polyphenol Research. 2017:143–170.
-
- Barreca D, Trombetta D, Smeriglio A, Mandalari G, Romeo O, Felice MR, Gattuso G, Nabavi SM: Food flavonols: Nutraceuticals with complex health benefits and functionalities. Trends Food Sci Technol 2021, 117:194–204.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

