Massive Trauma and Resuscitation Strategies
- PMID: 36872005
- PMCID: PMC10688568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anclin.2022.10.008
Massive Trauma and Resuscitation Strategies
Abstract
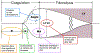
Massive trauma remains the leading cause of mortality among people aged younger than 45 years. In this review, we discuss the initial care and diagnosis of trauma patients followed by a comparison of resuscitation strategies. We discuss various strategies including use of whole blood and component therapy, examine viscoelastic techniques for management of coagulopathy, and consider the benefits and limitations of the resuscitation strategies and consider a series of questions that will be important for researchers to answer to provide the best and most cost-effective therapy for severely injured patients.
Keywords: Coagulopathy; Component therapy; Resuscitation; Trauma; Viscoelastic technique; Whole blood.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure None of the authors has any conflicts to disclose. Funding for this article was provided by R01GM127584 to B.M. Wagener.
Figures

References
-
- James D, Pennardt AM. Trauma Care Principles. StatPearls. 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

