Cadonilimab, a tetravalent PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody with trans-binding and enhanced target binding avidity
- PMID: 36872527
- PMCID: PMC10012886
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2180794
Cadonilimab, a tetravalent PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody with trans-binding and enhanced target binding avidity
Abstract
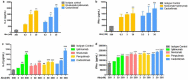
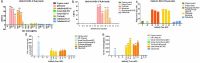
Clinical studies have shown that combination therapy of antibodies targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) significantly improves clinical benefit over PD-1 antibody alone. However, broad application of this combination has been limited by toxicities. Cadonilimab (AK104) is a symmetric tetravalent bispecific antibody with a crystallizable fragment (Fc)-null design. In addition to demonstrating biological activity similar to that of the combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies, cadonilimab possess higher binding avidity in a high-density PD-1 and CTLA-4 setting than in a low-density PD-1 setting, while a mono-specific anti-PD-1 antibody does not demonstrate this differential activity. With no binding to Fc receptors, cadonilimab shows minimal antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis, and interleukin-6 (IL-6)/IL-8 release. These features all likely contribute to significantly lower toxicities of cadonilimab observed in the clinic. Higher binding avidity of cadonilimab in a tumor-like setting and Fc-null design may lead to better drug retention in tumors and contribute to better safety while achieving anti-tumor efficacy.
Keywords: PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody; drug retention; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are all employees of Akeso Biopharma outside the submitted work.
Figures



References
-
- Morse MA, Overman MJ, Hartman L, Khoukaz T, Brutcher E, Lenz HJ, Atasoy A, Shangguan T, Zhao H, El-Rayes B.. Safety of nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab in previously treated microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2019;24:1453–61. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jäger D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F, et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:883–95. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30098-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Hammers HJ, Carducci MA, Salman P, Escudier B, Beuselinck B, Amin A, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1370–85. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30413-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
