The impact of distance education on readmission of patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36872565
- PMCID: PMC10277393
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.1698
The impact of distance education on readmission of patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To estimate the effect size of distance education on the readmission of patients with heart failure.
Design: This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Method: Both Persian and English interventional studies focused on investigating the effectiveness of any form of distance education interventions on the readmission of patients with heart failure were retrieved from the main databases: Embase, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, SID, and Google Scholar. Two independent teams screened the articles for eligibility. The Cochrane Risk of bias tool was implemented to evaluate the studies' quality. A random-effects model was applied to pool the effect sizes, I2 was calculated to examine heterogeneity, and Meta-regression was used to investigate the source of heterogeneity. The proposal was registered in the PROSPERO database (no. CRD42020187453).
Results: Articles 8836 were retrieved, and 11 articles were selected. Nine studies investigated the effect of distance education on readmission with <12-month follow-up (RR: 0.78 [95% CI 0.67-0.92]) and the I2 of 0.00%; and four studies examined the effect of distance intervention on readmission with 12-month or more follow-up (RR: 0.89 [95% CI 0.73-1.09]) and the I2 of 71.59%.
Keywords: distance education; heart failure; meta-analysis; readmission; systematic review.
© 2023 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare; that one of the included studies is the last author's research work (Reza Negarandeh).
Figures

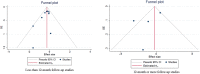
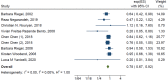
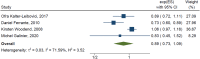
References
-
- Abdi, K. , Yaghobi, M. , Nouri, B. , & Karimian, A. (2021). Reasons of patient readmission in Sanandaj educational‐therapy in 2017. Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, 26(6), 83–92. 10.52547/SJKU.26.6.83 - DOI
-
- Bekelman, D. B. , Havranek, E. P. , Becker, D. M. , Kutner, J. S. , Peterson, P. N. , Wittstein, I. S. , Gottlieb, S. H. , Yamashita, T. E. , Fairclough, D. L. , & Dy, S. M. (2007). Symptoms, depression, and quality of life in patients with heart failure. Journal of Cardiac Failure, 13(8), 643–648. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bento, V. F. , & Brofman, P. R. (2009). Impact of the nursing consultation on the frequency of hospitalizations in patients with heart failure in Curitiba, Parana State. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia, 92(6), 454–460, 473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

