Emerging roles of miRNAs in neuropathic pain: From new findings to novel mechanisms
- PMID: 36873108
- PMCID: PMC9981676
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1110975
Emerging roles of miRNAs in neuropathic pain: From new findings to novel mechanisms
Abstract
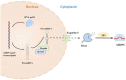
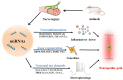
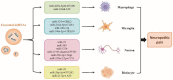
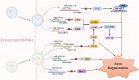
Neuropathic pain, which results from damage to the somatosensory nervous system, is a global clinical condition that affects many people. Neuropathic pain imposes significant economic and public health burdens and is often difficult to manage because the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. However, mounting evidence indicates a role for neurogenic inflammation and neuroinflammation in pain pattern development. There is increasing evidence that the activation of neurogenic inflammation and neuroinflammation in the nervous system contribute to neuropathic pain. Altered miRNA expression profiles might be involved in the pathogenesis of both inflammatory and neuropathic pain by regulating neuroinflammation, nerve regeneration, and abnormal ion channel expression. However, the lack of knowledge about miRNA target genes prevents a full understanding of the biological functions of miRNAs. At the same time, an extensive study on exosomal miRNA, a newly discovered role, has advanced our understanding of the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain in recent years. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of miRNA research and discusses the potential mechanisms of miRNAs in neuropathic pain.
Keywords: exosomes; miRNAs; neuroinflammation; neuropathic pain; review.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Wu, Zhu, Niu, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Newly discovered functions of miRNAs in neuropathic pain: Transitioning from recent discoveries to innovative underlying mechanisms.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069231225845. doi: 10.1177/17448069231225845. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38148597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinases as Mediators for miRNA Modulation of Neuropathic Pain.Cells. 2025 Apr 11;14(8):577. doi: 10.3390/cells14080577. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Vistas in microRNA Regulatory Interactome in Neuropathic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 25;12:778014. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.778014. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35280258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNA expression profile: a novel potential predictor for chronic nervous lesions.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014 Nov;46(11):942-9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmu090. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014. PMID: 25274330
-
Neuroinflammation Involved in Diabetes-Related Pain and Itch.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 20;13:921612. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.921612. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35795572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-Based Delivery Systems for Chronic Neuropathic Pain Treatment in Dorsal Root Ganglion.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 18;17(7):930. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070930. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA packaging into small extracellular vesicles and implications in pain.Pain Rep. 2024 Oct 23;9(6):e1198. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001198. eCollection 2024 Dec. Pain Rep. 2024. PMID: 39450410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropathic pain; what we know and what we should do about it.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 22;4:1220034. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1220034. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37810432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental enrichment for neuropathic pain via modulation of neuroinflammation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 Mar 21;18:1547647. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1547647. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40190342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-Derived Eye Drops for the Treatment of Corneal Neuropathic Pain.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jun;40(5):281-292. doi: 10.1089/jop.2023.0155. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38648544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amaechi O., Huffman M. M., Featherstone K. (2021). Pharmacologic therapy for acute pain. Am. Fam. Physician 104, 63–72. (Accessed July 1, 2021) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

