Impeding the combination of astrocytic ASCT2 and NLRP3 by talniflumate alleviates neuroinflammation in experimental models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 36873178
- PMCID: PMC9978855
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.07.021
Impeding the combination of astrocytic ASCT2 and NLRP3 by talniflumate alleviates neuroinflammation in experimental models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
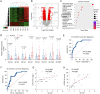
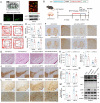
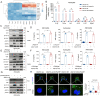
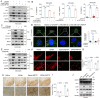
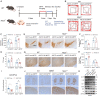
Alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2) is reported to participate in the progression of tumors and metabolic diseases. It is also considered to play a crucial role in the glutamate-glutamine shuttle of neuroglial network. However, it remains unclear the involvement of ASCT2 in neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease (PD). In this study, we demonstrated that high expression of ASCT2 in the plasma samples of PD patients and the midbrain of MPTP mouse models is positively correlated with dyskinesia. We further illustrated that ASCT2 expressed in astrocytes rather than neurons significantly upregulated in response to either MPP+ or LPS/ATP challenge. Genetic ablation of astrocytic ASCT2 alleviated the neuroinflammation and rescued dopaminergic (DA) neuron damage in PD models in vitro and in vivo. Notably, the binding of ASCT2 to NLRP3 aggravates astrocytic inflammasome-triggered neuroinflammation. Then a panel of 2513 FDA-approved drugs were performed via virtual molecular screening based on the target ASCT2 and we succeed in getting the drug talniflumate. It is validated talniflumate impedes astrocytic inflammation and prevents degeneration of DA neurons in PD models. Collectively, these findings reveal the role of astrocytic ASCT2 in the pathogenesis of PD, broaden the therapeutic strategy and provide a promising candidate drug for PD treatment.
Keywords: ASCT2; Astrocytes; Drug screening; Inflammation; NLRP3; Neurodegeneration; Parkinson's disease; Talniflumate.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kir6.1/K-ATP channel on astrocytes protects against dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease via promoting mitophagy.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Oct;81:509-522. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31288070
-
PPARß/δ agonist alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:483-489. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.06.005. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29885849
-
Inhibition of the hepatic Nlrp3 protects dopaminergic neurons via attenuating systemic inflammation in a MPTP/p mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jul 2;15(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1236-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29966531 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Microglial α-Synuclein/TLRs/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis in Parkinson's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:719807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719807. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in NURR1-Regulated Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16184. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416184. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome: contributions to inflammation-related diseases.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Jun 27;28(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00462-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37370025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ID1 expressing macrophages support cancer cell stemness and limit CD8+ T cell infiltration in colorectal cancer.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 23;14(1):7661. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43548-w. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37996458 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasomes in neurological disorders - mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Nat Rev Neurol. 2024 Feb;20(2):67-83. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00915-x. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38195712 Review.
-
Novel therapeutic targets to halt the progression of Parkinson's disease: an in-depth review on molecular signalling cascades.3 Biotech. 2023 Jul;13(7):218. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03637-5. Epub 2023 May 30. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37265542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia: interplay between the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and neuroinflammation.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1253273. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1253273. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37860013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Przedborski S. The two-century journey of Parkinson disease research. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Walsh J.G., Muruve D.A., Power C. Inflammasomes in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15:84–97. - PubMed
-
- Heneka M.T., McManus R.M., Latz E. Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19:610–621. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

