Echinacea purpurea-derived homogeneous polysaccharide exerts anti-tumor efficacy via facilitating M1 macrophage polarization
- PMID: 36873268
- PMCID: PMC9974447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100391
Echinacea purpurea-derived homogeneous polysaccharide exerts anti-tumor efficacy via facilitating M1 macrophage polarization
Abstract
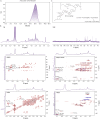
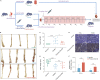
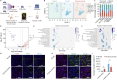
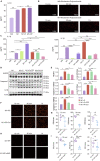
Echinacea purpurea modulates tumor progression, but the underlying mechanism is poorly defined. We isolated and purified a novel homogeneous polysaccharide from E. purpurea (EPPA), which was shown to be an arabinogalactan with a mean molecular mass (Mr) of 3.8 × 104 Da and with α- (1 → 5) -L-Arabinan as the backbone and α-L-Araf-(1→, →6)-β-D-Galp-(1→, and →4)-α-D-GalpA-(1→ as the side chains. Interestingly, oral administration of EPPA suppresses tumor progression in vivo and shapes the immune cell profile (e.g., facilitating M1 macrophages) in tumor microenvironment by single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis. More importantly, EPPA activates the inflammasome through a phagocytosis-dependent mechanism and rewires transcriptomic and metabolic profile, thereby potentiating M1 macrophage polarization. Collectively, we propose that EPPA supplementation could function as an adjuvant therapeutic strategy for tumor suppression.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wang Y., Wang Y., Ren Y., et al. Metabolic modulation of immune checkpoints and novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022;86:542–565. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas A.M., Pesic M., Engel E., et al. Inflammatory fibroblasts mediate resistance to neoadjuvant therapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 2022;40:168–184.e13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

