Nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1-mediated ribophagy protects T lymphocytes against apoptosis in sepsis
- PMID: 36873287
- PMCID: PMC9976742
- DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkac055
Nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1-mediated ribophagy protects T lymphocytes against apoptosis in sepsis
Abstract
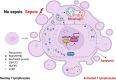
Background: Ribophagy is a selective autophagic process that specifically degrades dysfunctional or superfluous ribosomes to maintain cellular homeostasis. Whether ribophagy can ameliorate the immunosuppression in sepsis similar to endoplasmic reticulum autophagy (ERphagy) and mitophagy remains unclear. This study was conducted to investigate the activity and regulation of ribophagy in sepsis and to further explore the potential mechanism underlying the involvement of ribophagy in T-lymphocyte apoptosis.
Methods: The activity and regulation of nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1 (NUFIP1)-mediated ribophagy in T lymphocytes during sepsis were first investigated by western blotting, laser confocal microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Then, we constructed lentivirally transfected cells and gene-defective mouse models to observe the impact of NUFIP1 deletion on T-lymphocyte apoptosis and finally explored the signaling pathway associated with T-cell mediated immune response following septic challenge.
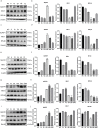
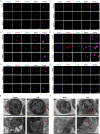
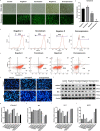
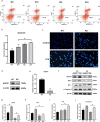
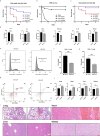
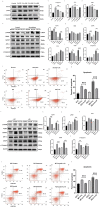
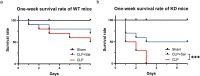
Results: Both cecal ligation and perforation-induced sepsis and lipopolysaccharide stimulation significantly induced the occurrence of ribophagy, which peaked at 24 h. When NUFIP1 was knocked down, T-lymphocyte apoptosis was noticeably increased. Conversely, the overexpression of NUFIP1 exerted a significant protective impact on T-lymphocyte apoptosis. Consistently, the apoptosis and immunosuppression of T lymphocytes and 1-week mortality rate in NUFIP1 gene-deficient mice were significantly increased compared with those in wild-type mice. In addition, the protective effect of NUFIP1-mediated ribophagy on T lymphocytes was identified to be closely related to the endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis pathway, and PERK-ATF4-CHOP signaling was obviously involved in downregulating T-lymphocyte apoptosis in the setting of sepsis.
Conclusions: NUFIP1-mediated ribophagy can be significantly activated to alleviate T lymphocyte apoptosis through the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway in the context of sepsis. Thus, targeting NUFIP1-mediated ribophagy might be of importance in reversing the immunosuppression associated with septic complications.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Autophagy; Immunosuppression; Lipopolysaccharide; Lymphocyte; Mitophagy; NUFIP1; Ribophagy; Sepsis.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NUFIP1-engineered exosomes derived from hUMSCs regulate apoptosis and neurological injury induced by propofol in newborn rats.Neurotoxicology. 2024 May;102:81-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2024.04.002. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Neurotoxicology. 2024. PMID: 38599287
-
NUFIP1 is a ribosome receptor for starvation-induced ribophagy.Science. 2018 May 18;360(6390):751-758. doi: 10.1126/science.aar2663. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Science. 2018. PMID: 29700228 Free PMC article.
-
The autophagic protein LC3 translocates to the nucleus and localizes in the nucleolus associated to NUFIP1 in response to cyclic mechanical stress.Autophagy. 2020 Jul;16(7):1248-1261. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1662584. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31476975 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle-specific autophagy in inflammatory diseases: a potential therapeutic target underlying the quality control of multiple organelles.Autophagy. 2021 Feb;17(2):385-401. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1725377. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 32048886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective autophagy as a therapeutic target for neurological diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(4):1369-1392. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03667-9. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33067655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Feb 18;20(1):20241104. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1104. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 39989614 Free PMC article.
-
Organellophagy regulates cell death:A potential therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases.J Adv Res. 2025 Apr;70:371-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 May 11. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38740259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms, biomarkers and signaling pathways associated with septic shock: from diagnosis to therapeutic targets.Burns Trauma. 2024 May 6;12:tkae006. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae006. eCollection 2024. Burns Trauma. 2024. PMID: 38716051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated dendritic cells in sepsis: functional impairment and regulated cell death.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 30;29(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00602-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38816685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

