Exploring the mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 36874006
- PMCID: PMC9975159
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1102581
Exploring the mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
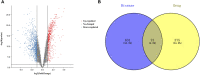
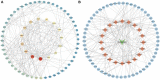
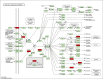
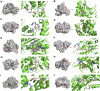
Objective: Curcumin is a plant polyphenol extracted from the Chinese herb turmeric. It was found that curcumin has good anti-cancer properties in a variety of cancers, but the exact mechanism is not clear. Based on the network pharmacology and molecular docking to deeply investigate the molecular mechanism of curcumin for the treatment of colon cancer, it provides a new research direction for the treatment of colon cancer. Methods: Curcumin-related targets were collected using PharmMapper, SwissTargetPrediction, Targetnet and SuperPred. Colon cancer related targets were obtained using OMIM, DisGeNET, GeneCards and GEO databases. Drug-disease intersection targets were obtained via Venny 2.1.0. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of drug-disease common targets were performed using DAVID. Construct PPI network graphs of intersecting targets using STRING database as well as Cytoscape 3.9.0 and filter core targets. Molecular docking via AutoDockTools 1.5.7. The core targets were further analyzed by GEPIA, HPA, cBioPortal and TIMER databases. Results: A total of 73 potential targets of curcumin for the treatment of colon cancer were obtained. GO function enrichment analysis yielded 256 entries, including BP(Biological Progress):166, CC(celluar component):36 and MF(Molecular Function):54. The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis yielded 34 signaling pathways, mainly involved in Metabolic pathways, Nucleotide metabolism, Nitrogen metabolism, Drug metabolism - other enzymes, Pathways in cancer,PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, etc. CDK2, HSP90AA1, AURKB, CCNA2, TYMS, CHEK1, AURKA, DNMT1, TOP2A, and TK1 were identified as core targets by Cytoscape 3.9.0. Molecular docking results showed that the binding energies of curcumin to the core targets were all less than 0 kJ-mol-1, suggesting that curcumin binds spontaneously to the core targets. These results were further validated in terms of mRNA expression levels, protein expression levels and immune infiltration. Conclusion: Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking initially revealed that curcumin exerts its therapeutic effects on colon cancer with multi-target, multi-pathway. Curcumin may exert anticancer effects by binding to core targets. Curcumin may interfere with colon cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating signal transduction pathways such as PI3K-Akt signaling pathway,IL-17 signaling pathway, Cell cycle. This will deepen and enrich our understanding of the potential mechanism of curcumin against colon cancer and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent studies.
Keywords: colon cancer; curcumin; immune infiltration; molecular docking; molecular mechanism; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2023 He, Liu, Wang, Rong, Zhu, Duan, Zheng and Mi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring the therapeutic mechanism of curcumin in prostate cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 19;10(12):e33103. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33103. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022084 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Targets and Molecular Mechanisms of Curcumin for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 May;67(5):2138-2159. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01190-x. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38822913
-
Exploring the mechanism of aloe-emodin in the treatment of liver cancer through network pharmacology and cell experiments.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 12;14:1238841. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1238841. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37900162 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the antitumor potential of cucurbitacin B in hepatocellular carcinoma through network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 21. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04273-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40397117 Review.
-
Effects of Curcumin on Radiation/Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis: Combined Meta-Analysis, Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 20;46(9):10545-10569. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090625. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Turmeric and Curcumin-Health-Promoting Properties in Humans versus Dogs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 26;24(19):14561. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914561. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin enhances ATG3-dependent autophagy and inhibits metastasis in cervical carcinoma.Cell Div. 2024 Nov 28;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00138-6. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 39609925 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-depression molecular mechanism elucidation of the phytochemicals in edible flower of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Oct 31;12(12):10164-10180. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4446. eCollection 2024 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723076 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology to investigate the effects of Yi-Qi-Xuan-Fei-Hua-Tan decoction for treating acute respiratory distress syndrome.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Feb 28;87(4):1969-1981. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003130. eCollection 2025 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40212228 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Prevention and Treatment with Polyphenols: Type IV Collagenase-Mediated Mechanisms.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;16(18):3193. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183193. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cerami E., Gao J., Dogrusoz U., Gross B. E., Sumer S. O., Aksoy B. A., et al. (2012). The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2, 401–404. 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-12-0095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

