Phenolic profile, in vitro antimicrobial and in vivo diuretic effects of endemic wild thyme Thymus comosus Heuff ex. Griseb. (Lamiaceae) from Romania
- PMID: 36874013
- PMCID: PMC9981668
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1115117
Phenolic profile, in vitro antimicrobial and in vivo diuretic effects of endemic wild thyme Thymus comosus Heuff ex. Griseb. (Lamiaceae) from Romania
Abstract
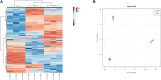
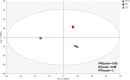
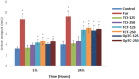
Thymus comosus Heuff ex. Griseb. (Lamiaceae) is a wild thyme species endemic for Romanian Carpathian areas, frequently collected as substitute for collective herbal product Serpylli herba, cited as antibacterial and diuretic remedy in traditional medicine. The present study aimed to evaluate the in vivo diuretic effect and in vitro antimicrobial properties of three herbal preparations (infusion-TCI, tincture-TCT and an hydroethanolic extract prepared through an optimized ultrasound-assisted method-OpTC) obtained from the aerial parts of T. comosus Heuff ex. Griseb, also evaluating their comprehensive phenolic profile. In vivo diuretic effect was tested using Wistar rats treated orally with each herbal preparation (125 and 250 mg/kg dispersed in 25 ml/kg isotonic saline solution) and quantified based on cumulative urine output (ml), diuretic action and diuretic activity. Additionally, sodium and potassium excretion were monitored using a potentiometric method with selective electrodes. In vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities were assessed using p-iodonitrotetrazolium chloride assay against six bacterial strains and six fungal strains by monitoring minimum inhibitory concentration (MICs), minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) and minimum fungicidal concentrations (MFCs). Finally, phenolic profile of the aforementioned herbal extracts was evaluated using an ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) method to check the impact of the different preparations on the most abundant and significant compounds. All the extracts exerted a mild diuretic action, TCT and OpTC inducing the most intense diuretic effect. Both herbal preparations produced a statistically significant, dose-dependent and gradual increase of the urine output, the effect being more intense at 24 h (6.63-7.13 ml/24 h). Potentiometric evaluation of urine samples collected from treated rats revealed a clear and mild natriuretic and kaliuretic effect after the administration. In terms of antimicrobial activity, E. coli (MIC-0.38 mg/ml), B. cereus (MIC-0.75 mg/ml)), Penicillium funiculosum and P. verrucosum var. cyclopium (MIC-0.19 mg/ml) showed the greater sensitivity to the tested extracts, respectively. UHPLC-HRMS screening showed that the bioactive potential of T. comosus herbal preparations was likely related to the higher amounts of phenolic acids (including rosmarinic acid), flavonoids (mainly flavones and derivatives) and other phenolics (such as different isomers of salvianolic acids) in their composition. The obtained results support the ethnopharmacological evidence regarding the mild diuretic and antibacterial potentials of the endemic wild thyme T. comosus, this study being the first one that assessed the aforementioned bioactivities for this species.
Keywords: Thymus comosus Heuff. ex. Griseb.; antimicrobials; diuretic; polyphenols; wild thyme.
Copyright © 2023 Babotă, Frumuzachi, Nicolescu, Stojković, Soković, Rocchetti, Zhang, Lucini, Crișan, Mocan and Voștinaru.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimized ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Thymus comosus Heuff. ex Griseb. et Schenk (wild thyme) and their bioactive potential.Ultrason Sonochem. 2022 Mar;84:105954. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.105954. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022. PMID: 35247683 Free PMC article.
-
Thymus Species from Romanian Spontaneous Flora as Promising Source of Phenolic Secondary Metabolites with Health-Related Benefits.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 6;12(2):390. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020390. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829949 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 28;8(11):515. doi: 10.3390/antiox8110515. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31661910 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive metabolic profile of phenolic acids and flavonoids in Glechomae Herba using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry with diagnostic ion filtering strategy.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Feb 5;164:615-629. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.11.017. Epub 2018 Nov 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 30469111
-
Wild thyme (Thymus serpyllum L.): a review of the current evidence of nutritional and preventive health benefits.Front Nutr. 2024 May 23;11:1380962. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1380962. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38846542 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Lamiaceae Plant Extracts: Inhibition of Bacterial Growth, Adhesion, Invasion, and Biofilm Formation and Degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 11;13(12):1616. doi: 10.3390/plants13121616. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931048 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Profiling and Therapeutic Potential of Thyme (Thymus spp.): A Medicinal Herb.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Nov 1;12(12):9893-9912. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4563. eCollection 2024 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPLC- and NMR-Based Chemical Profiling, Wound-Healing Potential, Anti-Inflammatory and Antibacterial Activities of Satureja pilosa (Lamiaceae), a Neglected Medicinal-Aromatic Herb.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;12(24):4114. doi: 10.3390/plants12244114. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140440 Free PMC article.
-
Bioassay-Guided Assessment of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Extracts from Medicinal Plants via High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography.Molecules. 2023 Oct 30;28(21):7346. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217346. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alarcón de la Lastra C., Martin M. J., Marhuenda E. (1987). Determination of the diuretic activity of various preparations of Thymus carnosus Boiss. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 45, 367–371. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3453614 . - PubMed
-
- Babotă M., Frumuzachi O., Gâvan A., Iacoviță C., Pinela J., Barros L., et al. (2022). Optimized ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Thymus comosus Heuff. ex Griseb. et Schenk (wild thyme) and their bioactive potential. Ultrason. Sonochem. 84, 105954. 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.105954 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

