Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity Associated with Moderate and Severe Disabilities: Results from the Study on Global AGEing and Adult Health (SAGE) Wave 2 in Ghana and South Africa
- PMID: 36874442
- PMCID: PMC9983501
- DOI: 10.5334/gh.1188
Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity Associated with Moderate and Severe Disabilities: Results from the Study on Global AGEing and Adult Health (SAGE) Wave 2 in Ghana and South Africa
Abstract
Background: Integrated management of cardiometabolic diseases is crucial in improving the quality of life of older persons. The objective of the study was to identify clusters of cardiometabolic multimorbidity associated with moderate and severe disabilities in Ghana and South Africa.
Methods: Data were from the World Health Organization (WHO) study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE) Wave-2 (2015) conducted in Ghana and South Africa. We analysed the clustering of cardiometabolic diseases including angina, stroke, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension with unrelated conditions such as asthma, chronic lung disease, arthritis, cataracts, and depression. The WHO Disability Assessment Instrument version 2.0 was used to assess functional disability. We used latent class analysis to calculate the multimorbidity classes and disability severity levels. Ordinal logistic regression was used to identify the clusters of multimorbidity associated with moderate and severe disabilities.
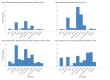
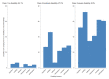
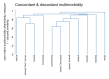
Results: Data from 4,190 adults aged over 50 years were analysed. The prevalence of moderate and severe disabilities was 27.0% and 8.9% respectively. Four latent classes of multimorbidity were identified. These included a relatively healthy group with minimal cardiometabolic multimorbidity (63.5%), general and abdominal obesity (20.5%), hypertension, abdominal obesity, diabetes, cataracts, and arthritis (10.0%), and angina, chronic lung disease, asthma, and depression (6.0%). Compared to the participants with minimal cardiometabolic multimorbidity, the odds of moderate and severe disabilities were higher among participants with multimorbidity comprising hypertension, abdominal obesity, diabetes, cataract and arthritis [aOR = 3.0; 95% CI 1.6 to 5.6], and those with angina, chronic lung disease, asthma and depression [aOR = 2.7; 95% CI 1.6 to 4.5].
Conclusions: Cardiometabolic diseases among older persons in Ghana and South Africa cluster in distinct multimorbidity patterns that are significant predictors of functional disabilities. This evidence may be useful for defining disability prevention strategies and long-term care for older persons living with or at risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in sub-Saharan Africa.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic diseases; disability; latent class analysis; multimorbidity.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Arokiasamy P, Uttamacharya U, Jain K, Biritwum RB, Yawson AE, Wu F, et al. The impact of multimorbidity on adult physical and mental health in low-and middle-income countries: what does the study on global ageing and adult health (SAGE) reveal? BMC medicine. 2015; 13(1): 1–16. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-015-0402-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vos T, Lim SS, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi M, Abbasifard M, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. 2020; 396(10258): 1204–22. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naghavi M, Abajobir AA, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet. 2017; 390(10100): 1151–210. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

