Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia in Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- PMID: 36874752
- PMCID: PMC9976640
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.34386
Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia in Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
Abstract
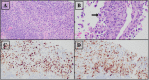
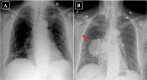
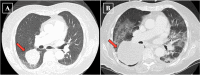
It is well-documented that lung and bronchus cancers are the leading cause of cancer death in the United States in both male and female patients, with lung adenocarcinoma accounting for the highest prevalence of lung cancers. Significant eosinophilia in the setting of lung adenocarcinoma has been documented in a few reports, being described as a rare paraneoplastic syndrome. We report on an 81-year-old female with hypereosinophilia-associated lung adenocarcinoma. A chest film showed a right lung mass, which was not apparent on a chest film 1 year prior, in the setting of significant leukocytosis of 27.90 x 103/mm3 with eosinophilia of 6.40 x 103/mm3. A computed tomography (CT) chest, obtained during admission, demonstrated significant right lower lobe mass enlargement since the previous study completed 5 months prior, with new occlusion of bronchi and pulmonary vessels to the region of the mass. Our observations are consistent with prior reports showing that the presence of eosinophilia in lung cancers may indicate rapid disease progression.
Keywords: hypereosinophilia; lung adenocarcinoma; paraneoplastic hypereosinophilia; paraneoplastic syndrome; poorly differentiated lung adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2023, Ream et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, United States Cancer Statistics: Data Visualizations. [ Aug; 2022 ]. 2022. https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/ https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/
-
- Non-small-cell lung cancer associated with excessive eosinophilia and secretion of interleukin-5 as a paraneoplastic syndrome. Pandit R, Scholnik A, Wulfekuhler L, Dimitrov N. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:234–237. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
