Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on postpartum depression: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36874857
- PMCID: PMC9976935
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.990162
Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on postpartum depression: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
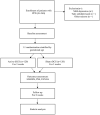
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a complex combination of physiological, emotional, and behavioral alterations associated with postpartum chemical, social, and psychological variations. It does harm to the relationship between family members that could potentially last for years. However, standard depression treatments are not ideal for PPD, and the outcomes of these treatments are debatable. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is an emerging technology that could provide patients with PPD with a safe and non-pharmacological treatment. tDCS can relieve depression by directly stimulating the prefrontal cortex through the excitatory effect of the anode. It may also ease depression indirectly by promoting the production and release of the neurotransmitter GABA. The mechanism of tDCS makes it an ideal therapeutic approach to treat PPD, although it has not been widely used, and its effect has not been evaluated systematically and effectively. A double-blind, randomized controlled trial will be conducted involving 240 tDCS-naive patients with PPD, who will be randomly divided into two groups. One group will receive routine clinical treatment and care with active tDCS, and the other group will receive routine clinical treatment and care with sham tDCS. Each group of patients will receive a 3-week intervention during which they will receive 20 min of active or sham tDCS 6 days per week. The Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale will be administered before the intervention as a baseline and on each weekend throughout the intervention phase. Before and after the intervention, the Perceived Stress Scale and the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule will be evaluated. Side effects and abnormal reactions will be recorded during each treatment. As antidepressants are banned in the study, the results will not be affected by drugs and will therefore be more accurate. Nonetheless, this experiment will be conducted in a single center as a small sample experiment. Therefore, future studies are required to confirm the effectiveness of tDCS in treating PPD.
Keywords: mental health; postpartum depression; randomized controlled trial; study protocol; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Kang, Dong, Zeng, Zou, Su, Zhang, Liu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Neurostimulation of the Brain in Depression Trial: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Treatment-Resistant Depression.JMIR Res Protoc. 2021 Mar 17;10(3):e22805. doi: 10.2196/22805. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33729165 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of adjunctive intensive transcranial direct current stimulation of different cortices in treatment-resistant depression: a study protocol for a randomized double-blinded sham-controlled trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 19;22(1):802. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-04465-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36536362 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on patients with post-stroke fatigue: a study protocol for a double-blind randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Mar 5;23(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06128-9. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35248120 Free PMC article.
-
PsychotherapyPlus: augmentation of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with prefrontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in major depressive disorder-study design and methodology of a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018 Dec;268(8):797-808. doi: 10.1007/s00406-017-0859-x. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29214483
-
Prefrontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) as treatment for major depression: study design and methodology of a multicenter triple blind randomized placebo controlled trial (DepressionDC).Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Dec;267(8):751-766. doi: 10.1007/s00406-017-0769-y. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28246891 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Abdelnaim M. A., Langguth B., Deppe M., Mohonko A., Kreuzer P. M., Poeppl T. B., et al. . (2020). Anti-suicidal efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in depressive patients: a retrospective analysis of a large sample. Front. Psychiatry 10, 929. 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00929 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An S., Fousek J., Kiss Z. H., Cortese F., van Der Wijk G., McAusland L. B., et al. . (2022). High-resolution virtual brain modeling personalizes deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: Spatiotemporal response characteristics following stimulation of neural fiber pathways. Neuroimage. 249, 118848. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118848 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

