Immune-related risk score: An immune-cell-pair-based prognostic model for cutaneous melanoma
- PMID: 36875110
- PMCID: PMC9975150
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1112181
Immune-related risk score: An immune-cell-pair-based prognostic model for cutaneous melanoma
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is among the most malignant immunologic tumor types and is associated with high mortality. However, a considerable number of melanoma patients cannot benefit from immunotherapy owing to individual differences. This study attempts to build a novel prediction model of melanoma that fully considers individual differences in the tumor microenvironment.
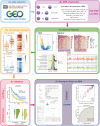
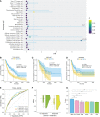
Methods: An immune-related risk score (IRRS) was constructed based on cutaneous melanoma data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was used to calculate immune enrichment scores of 28 immune cell signatures. We performed pairwise comparisons to obtain scores for cell pairs based on the difference in the abundance of immune cells within each sample. The resulting cell pair scores, in the form of a matrix of relative values of immune cells, formed the core of the IRRS.
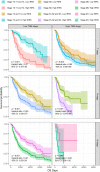
Results: The area under the curve (AUC) for the IRRS was over 0.700, and when the IRRS was combined with clinical information, the AUC reached 0.785, 0.817, and 0.801 for the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival, respectively. Differentially expressed genes between the two groups were enriched in staphylococcal infection and estrogen metabolism pathway. The low IRRS group showed a better immunotherapeutic response and exhibited more neoantigens, richer T-cell receptor and B-cell receptor diversity, and higher tumor mutation burden.
Conclusion: The IRRS enables a good prediction of prognosis and immunotherapy effect, based on the difference in the relative abundance of different types of infiltrating immune cells, and could provide support for further research in melanoma.
Keywords: cell pair; cutaneous melanoma; immunotherapy response; prognosis model; tumor infiltrating immune cell.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Long, Bu, Zhang, Deng, Liu, Su and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer MP declared a shared affiliation with the authors ML, XL, GZ, GD, YL, JS and KH to the handling editor at time of review.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

