Respiratory virus circulation during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Household Influenza Vaccine Evaluation (HIVE) cohort
- PMID: 36875204
- PMCID: PMC9975790
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.13106
Respiratory virus circulation during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Household Influenza Vaccine Evaluation (HIVE) cohort
Abstract
Background: The annual reappearance of respiratory viruses has been recognized for decades. COVID-19 mitigation measures taken during the pandemic were targeted at respiratory transmission and broadly impacted the burden of acute respiratory illnesses (ARIs).
Methods: We used the longitudinal Household Influenza Vaccine Evaluation (HIVE) cohort in southeast Michigan to characterize the circulation of respiratory viruses from March 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021, using RT-PCR of respiratory specimens collected at illness onset. Participants were surveyed twice during the study period, and SARS-CoV-2 antibodies were measured in serum by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. Incidence rates of ARI reports and virus detections were compared between the study period and a preceding pre-pandemic period of similar duration.
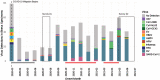
Results: Overall, 437 participants reported a total of 772 ARIs; 42.6% had respiratory viruses detected. Rhinoviruses were the most frequent virus, but seasonal coronaviruses, excluding SARS-CoV-2, were also common. Illness reports and percent positivity were lowest from May to August 2020, when mitigation measures were most stringent. Seropositivity for SARS-CoV-2 was 5.3% in summer 2020 and increased to 11.3% in spring 2021. The incidence rate of total reported ARIs for the study period was 50% lower (95% CI: 0.5, 0.6; p < 0.001) than the incidence rate from a pre-pandemic comparison period (March 1, 2016, to June 30, 2017).
Conclusions: The burden of ARI in the HIVE cohort during the COVID-19 pandemic fluctuated, with declines occurring concurrently with the widespread use of public health measures. Rhinovirus and seasonal coronaviruses continued to circulate even when influenza and SARS-CoV-2 circulation was low.
Keywords: COVID‐19; household cohort; influenza; respiratory virus; serological surveillance.
© 2023 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
ETM reports grant funding from Merck outside of the submitted work.
Figures
Update of
-
Respiratory Virus Circulation during the First Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Household Influenza Vaccine Evaluation (HIVE) Cohort.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Dec 9:2022.12.08.22283268. doi: 10.1101/2022.12.08.22283268. medRxiv. 2022. Update in: Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2023 Mar 01;17(3):e13106. doi: 10.1111/irv.13106. PMID: 36523413 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

