An overview of probiotic health booster-kombucha tea
- PMID: 36875441
- PMCID: PMC9975612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.010
An overview of probiotic health booster-kombucha tea
Abstract
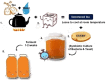
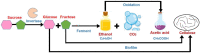
Traditional herbal medicine (THM) is a significant division of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that plays an important role in maintaining health and disease prevention. WHO has consistently highlighted the significance of traditional, complementary, and alternative medicine in human healthcare. Most people in Eastern Asia will start their day with a cup of tea. The tea provides a nourishing effect, and it has become an inevitable part of life. There are several types of tea, like black tea, green tea, oolong tea, white tea, and herbal tea. Besides the refreshments, it is important to consume beverages that benefit health. One such alternative is a healthy probiotic drink called kombucha, a fermented tea. Kombucha tea is aerobically fermented by infusing sweetened tea with a cellulose mat/ pellicle called SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast). Kombucha is a source of bioactive compounds that include organic acids and amino acids, vitamins, probiotics, sugars, polyphenols, and antioxidants. Currently, studies on kombucha tea and SCOBY are gaining attention for their remarkable properties and applications in the food and health industries. The review gives an overview of the production, fermentation, microbial diversity, and metabolic products of kombucha. The possible implications for human health are also discussed.
Keywords: bio-tea; fermentation; fermented beverage; kombucha; probiotics; symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast; tea fungus.
© 2022 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Adriani L., Mayasari N., Kartasudjana R. The effect of feeding fermented kombucha tea on HLD, LDL and total cholesterol levels in the duck bloods. Biotechnology in Animal Husbandry. 2011;27(4):1749–1755.
-
- Balentine D.A. Manufacturing and chemistry of tea. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1992;8:102–117.
-
- Banerjee D., Hassarajani S.A., Maity B., Narayan G., Bandyopadhyay S.K., Chattopadhyay S. Comparative healing property of kombucha tea and black tea against indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration in mice: Possible mechanism of action. Food & Function. 2010;1(3):284–293. - PubMed
-
- Battikh H., Bakhrouf A., Ammar E. Antimicrobial effect of Kombucha analogues. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 2012;47(1):71–77.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

